* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
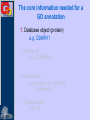
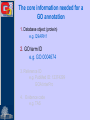
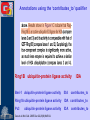
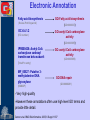
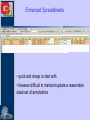
Methods for Creating GO Annotations Emily Dimmer European Bioinformatics Institute Wellcome Trust Genome Campus Cambridge UK The core information needed for a GO annotation 1. Database object (protein) e.g. Q9ARH1 2. GO term ID e.g. GO:0004674 3. Reference ID e.g. PubMed ID: 12374299 GOA:InterPro 4. Evidence code e.g. TAS The core information needed for a GO annotation 1. Database object (protein) e.g. Q9ARH1 2. GO term ID e.g. GO:0004674 3. Reference ID e.g. PubMed ID: 12374299 GOA:InterPro 4. Evidence code e.g. TAS The core information needed for a GO annotation 1. Database object (protein) e.g. Q9ARH1 2. GO term ID e.g. GO:0004674 3. Reference ID e.g. PubMed ID: 12374299 GOA:InterPro 4. Evidence code e.g. TAS The core information needed for a GO annotation 1. Database object (protein) e.g. Q9ARH1 2. GO term ID e.g. GO:0004674 3. Reference ID e.g. PubMed ID: 12374299 GOA:InterPro 4. Evidence code e.g. TAS GO Evidence Codes • Every GO annotation includes an Evidence Code that gives information about the evidence from which the annotation has been made. Code Definition IEA Inferred from Electronic Annotation IDA Inferred from Direct Assay IEP Inferred from Expression Pattern IGI Inferred from Genetic Interaction IMP Inferred from Mutant Phenotype IPI Inferred from Physical Interaction ISS Inferred from Sequence Similarity TAS Traceable Author Statement NAS Non-traceable Author Statement RCA Reviewed Computational Analysis IC Inferred from Curator ND No Data Manually annotated Additional fields can be used to further clarify an annotation • Qualifiers (NOT, contributes_to, colocalizes_with) • ‘with’ data to provide users with more information on the method/experiment applied. Annotations using the ‘NOT’ qualifier hSNF2H Rsf-1 NOT ATPase activity GO:0016887 IDA ATPase activity GO:0016887 IDA Loyola et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Oct;23(19):6759-68. Annotations using the ‘contributes_to’ qualifier A protein which is part of a complex can be annotated to terms in that describe: 1. Its individual action 2. the action of the whole complex (Molecular Function terms) To differentiate between these two types of annotations, if a protein does not possess the activity itself, the annotation has the contributes_to qualifier added Annotations using the ‘contributes_to’ qualifier Ring1B ubiquitin-protein ligase activity IDA Bmi-1 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity IDA Ring1A ubiquitin-protein ligase activity IDA contributes_to Pc3 IDA ubiquitin-protein ligase activity Cao et al. Mol Cell. 2005 Dec 22;20(6):845-54. contributes_to contributes_to Annotations using the ‘colocalizes_with’ qualifier • Used with cellular component terms • To describe proteins that are transiently or peripherally associated with an organelle or complex CENP-E condensed chromosome kinetochore IDA colocalizes_with Meyer et al. J Cell Biol. 1997 Feb 24;136(4):775-88. Annotations using additional identifiers in the ‘with’ column • Provides further information to support the evidence code used in an annotation When transferring annotations based on sequence similarity… Protein GO term Evidence Reference With For protein binding annotations… Protein GO term Evidence Reference With There are two main types of GO annotation: Electronic Annotation Manual Annotation both these methods have their advantages They can be easily distinguished by the ‘evidence code’ used. Electronic Annotation Fatty acid biosynthesis GO:Fatty acid biosynthesis ( Swiss-Prot Keyword) EC:6.4.1.2 (EC number) (GO:0006633) GO:acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity (GO:0003989) IPR000438: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase carboxyl transferase beta subunit (InterPro entry) MF_00527: Putative 3methyladenine DNA glycosylase GO:acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity (GO:0003989) GO:DNA repair (HAMAP) • (GO:0006281) Very high-quality •However these annotations often use high-level GO terms and provide little detail. Camon et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005; 6 Suppl 1:S17 Mappings of external concepts to GO http://www.geneontology.org/GO.indices.shtml InterProScan http://www.ebi.ac.uk/InterProScan Output from InterProScan… Manual Annotation • High–quality, specific annotations made using: • Peer-reviewed papers • A range of evidence codes to categorize the types of evidence found in a paper • very time consuming and requires trained biologists Finding GO terms … …for chicken TaxREB107protein (Q8UWG7) nucleoli cytoplasmic increased troponin I reporter gene activity positive modulator of skeletal muscle gene expression Component: cytoplasm GO:0005737 Component: nucleolus GO:0005730 positive regulation of transcription GO:0045941 Process: Process: positive regulation of skeletal muscle development GO:0048643 http://www.geneontology.org/GO.annotation.shtml Aids for GO manual annotation Many are on the GO Consortium tools page: http://www.geneontology.org/GO.tools.shtml GoPubMed gives an overview over literature abstracts taken from PubMed and categorizes them with Gene Ontology terms: GoPubMed http://gopubmed.org GoPubMed http://gopubmed.org http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Rebholz-srv/whatizit Whatizit UniProt Ac’s GO terms http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Rebholz-srv/whatizit Searching for GO terms http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ego http://www.godatabase.org http://www.geneontology.org/GO.tools.html …and more varieties of browsers available on the GO Tools page: http://www.geneontology.org/GO.tools.html http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ego Exact match http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ego GO annotation editors • The GO Consortium is aware there is a need for a light-weight, generic GO annotation tool. • enhanced spreadsheets (e.g. Excel) • Protein2GO (GOA) Enhanced Spreadsheets • quick and cheap to start with • however difficult to maintain/update a reasonable sized set of annotations protein2go Protein2GO Protein2GO Protein2GO Protein2GO Protein2GO Protein2GO Protein2GO How users can view GO annotations Download and parse an entire gene association file… …or look at annotations for a protein using one of the GO browsers or a database that integrates GO annotations. QuickGO : http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ego http://www.geneontology.org/GO.current.annotations.shtml http://www.ebi.ac.uk/goa Acknowledgements Nicky Mulder Head of InterPro Evelyn Camon Daniel Barrell Rachael Huntley GOA Coordinator GOA Programmer GOA Curator David Binns & John Maslen QuickGO, Protein2GO tools Achuthanunni C. Balakrishnan Text-2-GO Jorge Duarte IPI sets Midori Harris Jane Lomax Amelia Ireland Jennifer Clarke GO Editor GO Curator GO Curator GO Curator Rolf Apweiler Head of Sequence Database Group The Gene Ontology Consortium and 1.5 members of GOA currently supported by an P41 grant from the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) [grant HG002273], GOA is also supported by core EMBL funding.