* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download An easy-to-use, web-based DNA annotation platform
Craig Venter wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mycoplasma laboratorium wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene Disease Database wikipedia , lookup
Bioinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
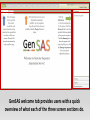
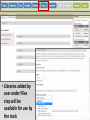
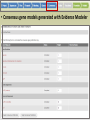
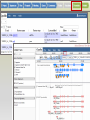
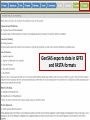
Genome Sequence Annotation Server An easy to use, web-based solution for specialty crop genome annotation Jodi Humann, Stephen Ficklin, Taein Lee, Chun-Huai Cheng, Sook Jung, Jill Wegrzyn, David Neale and Dorrie Main Genome annotation • Assigns biological relevance to DNA sequences • Structural: Gene elements (i.e. ORFs, repeats, introns/exons, RNAs) • Functional: Biological information, biochemical/physiological function of genes • Many tools available, but run independently of each other • Most of the tools are run via the command line and require server access What scientists want • A platform that: • Is a single location for DNA annotation • Does not require management of computing equipment and software tools • Is easy to use • Can be adapted to a variety of DNA sequences What is GenSAS? • A single website that combines numerous annotation tools into one interface • Compatible with Firefox, Chrome, Internet Explorer • User accounts keep data private and secure as well as allow users to share data for collaborative annotation • Easy-to-use interfaces, with integrated instructions allow researchers at all skill levels to annotate DNA http://gensas.bioinfo.wsu.edu/ GenSAS welcome tab provides users with a quick overview of what each of the three screen sections do. • Project is created and information about organism is entered. Users can also provide info about genome assembly version. • Single sequence or multiple-sequence FASTA files are uploaded and are associated with the project • All sequences in multisequence FASTA file are analyzed with the same parameters • The addition of support files increase the accuracy of the annotation and curation • Previous annotations can also be uploaded for comparison with new data • RepeatMasker – evidence based repeat finder • RepeatModeler – de novo repeat finder • Can run each tool multiple times with different parameters • User then can look at the results and choose which set(s) to use in the masked consensus • Masked consensus is then used as input for the annotation tools unless the user elects to skip repeat masking • Libraries added by user under Files step will be available for use by the tools • Consensus gene models generated with Evidence Modeler • Job status can be monitored through Job Queue • Progress through GenSAS is automatically saved • Users can log off GenSAS and jobs will continue running • While jobs are running, users can look at the completed results in WebApollo/JBrowse • Once the project has results, users can share the project with other GenSAS users for collaborative annotation GenSAS exports data in GFF3 and FASTA formats GenSAS v4.0 coming soon • Will allow GenSAS to submit jobs to compute cluster to allow for annotation of larger genomes • PASA has been integrated to improve and refine gene models • Functional annotation tools have been added (InterProScan, Pfam, SignalP, TargetP) Supported by