* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sex Linked Inheritance
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
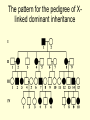
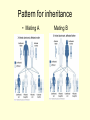
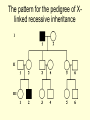
Sex Linked Inheritance • A human female, has 23 pair of chromosomes • A human male, has 22 similar pairs and one pair consisting of two chromosomes that are dissimilar in size and structure. • The 23 rd pair in both the sexes is called sex chromosomes • the female, XX. the male, XY X-linked diseases • X-linked diseases are those for which the gene is present on the X chromosome. • X-linked genes are never passed from father to son. • The Y chromosome is the only sex chromosome that passes from father to son. • Males are never carriers – if they have a mutated gene on the X chromosome, it will be expressed. X-linked dominant • Hereditary pattern in which a dominant gene on the X chromosome causes a characteristic to be manifested in the offspring. • X-linked dominant diseases are those that are expressed in females when only a single copy of the mutated gene is present. • Very few X-linked dominant diseases have been identified (e.g. hypophosphatemic rickets, Alport syndrome, diabetes insipidus) – hypophosphatemic rickets or vitamin D resistant rickets >>>low serum phosphorus, skeletal abnormalities – Alport syndrome, which involves progressive hearing loss and progressive kidney problems. Characteristics of X-linked dominant diseases include: • Never passed from father to son. • Affected males produce only affected females. An affected male only has one X chromosome to pass on to his daughters • Affected females produce 50% normal and 50% affected offspring.. >>>> heterozygous • Males are usually more severely affected than females. Some X-linked dominant traits may even be lethal to males. • Females are more likely to be affected. Since females have 2 X chromosomes, they have 2 “chances” to inherit the mutated allele. The pattern for the pedigree of Xlinked dominant inheritance Pattern for inheritance • Mating A Mating B Pattern for inheritance • Mating A Mating B X-linked recessive • hereditary pattern in which a recessive gene on the X chromosome results in the manifestation of characteristics in male offspring and a carrier state in female offspring • X-linked recessive diseases are those in which a female must have two copies of the mutant allele in order for the mutant phenotype to develop. • Many X-linked recessive disorders are wellknown, including color blindness, hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The pattern for the pedigree of Xlinked recessive inheritance • • www.tylermedicalclinic.com/ pgd-presentation18... Pattern of x linked recessive inheritance staff.um.edu.mt/ acus1/02Monogenic.htm Hemophilia • The blood fails to clot normally • Lacking a blood clotting factor VIII(antihemophilic globulin, AHG),IX • bleeding from even minor cuts • in 1,500 newborn males. Most (75%) have hemophilia A, a lack of clotting factor VIII. • Hemophilia B- "Christmas Disease" is a defect in clotting factor IX. • Transfusions of fresh whole blood or plasma or factor concentrates control bleeding Hemophilia A and B. Coagulation system www.emedicine.com/.../ 14801480ped0962-01.jpg Inheritance of hemophilia www.hemophilia.ca/ en/images/figure5.gif A Pedigree of Hemophilia in the Royal Families of Europe Typical features of X-linked recessive inheritance • Never passed from father to son. • Males are much more likely to be affected because they only need one copy of the mutant allele to express the phenotype. • • Affected males get the disease from their mothers and all of their daughters are obligate carriers. • Sons of heterozygous females have a 50% chance of receiving the mutant allele. • These disorders are typically passed from an affected grandfather to 50% of his grandsons.