* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
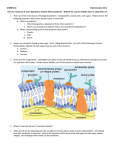
Cyclization of Aldoses and Ketoses Reaction of an alcohol with: (a) An aldehyde to form a hemiacetal (b) A ketone to form a hemiketal Cyclization of D-glucose to form glycopyranose • Fischer projection (top left) • Threedimensional figure (top right) • C-5 hydroxyl close to aldehylde group (lower right) • Reaction of C-5 hydroxyl with one side of C-1 gives a, reaction with the other side gives b Cyclization of D-ribose to form a- and b-D-ribopyranose and a- and b-Dribofuranose Deoxy Sugars • In deoxy sugars an H replaces an OH Amino Sugars • An amino group replaces a monosaccharide OH • Amino group is sometimes acetylated • Amino sugars of glucose and galactose occur commonly in glycoconjugates Sugar acids derived from glucose • L-Ascorbic acid is derived from D-glucuronate Structures of Disaccharides Structures of (a) maltose, (b) cellobiose Structures of (c) lactose, (d) sucrose Reducing and Nonreducing Sugars • Monosaccharides and most disaccharides are hemiacetals (contain a reactive carbonyl group) • Called reducing sugars because they can reduce metal ions (Cu2+, Ag+) • Examples: glucose, maltose, cellobiose, lactose Polysaccharides • Homoglycans - homopolysaccharides containing only one type of monosaccharide • Heteroglycans - heteropolysaccharides containing residues of more than one type of monosaccharide • Lengths and compositions of a polysaccharide may vary within a population of these molecules Starch and Glycogen • D-Glucose is stored intracellularly in polymeric forms • Plants and fungi - starch • Animals - glycogen • Starch is a mixture of amylose (unbranched) and amylopectin (branched) Structure of amylopectin Glycoconjugates • Heteroglycans appear in three types of glycoconjugates: Proteoglycans Peptidoglycans Glycoproteins Proteoglycans • Proteoglycans - glycosaminoglycan-protein complexes • Glycosaminoglycans - unbranched heteroglycans of repeating disaccharides (many sulfated hydroxyl and amino groups) • Disaccharide components include: (1) amino sugar (D-galactosamine or D-glucosamine), (2) an alduronic acid Repeating disaccharide of hyaluronic acid • GlcUA = D-glucuronate • GlcNAc= N-acetylglucosamine Proteoglycan aggregate of cartilage Peptidoglycans • Peptidoglycans - heteroglycan chains linked to peptides • Major component of bacterial cell walls • Heteroglycan composed of alternating GlcNAc and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) • b-(1 4) linkages connect the units Glycan moiety of peptidoglycan Structure of the peptidoglycan of S. aureus (a) Repeating disaccharide unit, (b) Cross-linking of the peptidoglycan macromolecule Structure of peptidoglycan Cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria Gram-negative bacteria Penicillin inhibits a transpeptidase involved in bacterial cell wall formation • Fig 8.32 Structures of penicillin and -D-Ala-D-Ala • Penicillin structure resembling -D-AlaD-Ala is shown in red HN HN O N H H N O Enz1 O N H O H O N N H O O D-ala O N H H N O N H O O H O N Enz1 CONH 2 CONH 2 O O H H N N N N O H O H O Enz1 ? H N O O S N CO 2H NH 3 Penicillin G amoxicillin ampicillin methicillin dicloxaicillin flucloxacillin cefalexin imipenem clavulanic acid