* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria powerpoint notes
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
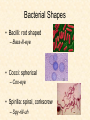
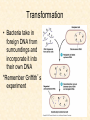
Bacteria Bacteria • Unicellular • Prokaryotes • Cells walls containing peptidoglycan Bacterial Shapes • Bacilli: rod shaped – Bass-ill-eye • Cocci: spherical – Cox-eye • Spirilla: spiral, corkscrew – Spy-rill-uh What are the differences between eubacteria and archaebacteria? Eubacteria versus Archaebacteria • Cell walls of Eubacteria have lots peptidoglycans (mesh of sugar and amino acids) – Archaebacteria do not • Archaebacteria often live in very extreme environments (hot springs, digestive tracts, Great Salt Lake, etc.) Metabolism • Bacteria can be heterotrophic or autotrophic – Remember: autotrophs are not ALL photosynthesizers! – Some are chemosynthesizers (convert carbon into organic compounds) How Bacteria Reproduce: Binary Fission • When a bacterium has doubled in size, it replicates its DNA and divides in half • Sexual or asexual? • Identical or different daughter cells? If bacteria are identical, how do they evolve? Where does genetic variety come from (besides natural mutation rate)? Genetic Variety in Bacteria • Conjugation: cell-to-cell contact • Transformation: bacterium takes up foreign DNA from surrounding environment • Transduction: DNA is transferred from one bacterial cell to another by a virus Conjugation • A hollow bridge (pilus) forms between two bacteria and genes move from one cell to the other • Increases genetic diversity of a population Conjugation Transformation • Bacteria take in foreign DNA from surroundings and incorporate it into their own DNA *Remember Griffith’s experiment Transduction • DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus • When new bacteriophages are made, they may contain a small amount of the host cell’s DNA Benefits of Bacteria • Some are producers that undergo photosynthesis • Some are decomposers that break down dead matter to recycle the nutrients • Some convert nitrogen gas to a form that can be used by plants (nitrogen fixation) What are some dangers of bacteria? Dangers of Bacteria • Break down cells and tissues for food Example: Tuberculosis (destroys lung tissue) • Release toxins (poisons) that travel through the body Example: Streptococcus releases toxins into the blood stream causes strep throat and scarlet fever