* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 222-1
Metabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
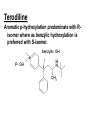
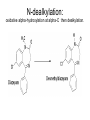
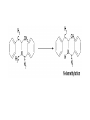
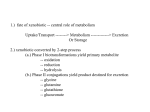
Drug Metabolism and Prodrugs Drug metabolism is the transformation of foreign compounds ( xenobiotics) into water soluble derivatives which can easily eliminate via renal route. Xenobiotics ( non essential exogenous, foreign compounds ) • This applies particularly to chemical compounds which enter the organism and don't serve as nutrient or other essential factors. • Xenobiotics can not be allowed to concentrate beyond limits in a living system, but must be eliminate by excretion. • Drug metabolism may be regarded as detoxification processes in some cases. • Not all metabolites are non toxic Example As a rule, the metabolism of xenobiotics takes place in two steps known as phase I & phase II reactions Phase I ( functionalization reaction ) Is the process of increasing of the hydrophilicity of lipophilic drug by introducing polar functional group eg; oH,cooH,NH2,SH to the molecule through oxidative reductive & hydrolytic biotransformation. Phase II ( conjugation reactions ) • Link an endogenous solubilizing moiety either to the original drug (if polar function are already present) or to the phase I metabolite. • Common solubilizing groups are glucuronic acid, various amino acids or sulphate groups. • The conjugate molecule, being more polar and water-soluble, is usually excreted via the renal route Effect of metabolism on the therapeutic activity of drugs Conclusion • Drug metabolism or biotransformation are the chemical reactions that are responsible for the conversion of drugs into other products within the body before and after they have reached their sites of action. • Almost all of these reactions are enzyme catalyzed. • A knowledge of the concepts of drug metabolism is useful in both the design of new drugs and the improvement of existing drugs. Factors affecting drug metabolism • • • • Genetic factors Physiological factors Pharmaceutical factors Drug interactions Genetic factors Biological half –life (t1/2) of various drugs Physiological factors eg: Age which is the ability of the body to metabolize the drug lower in v. young & eldery. Pharmacodynamic factors • The dose, the route and the frequency of administration of drugs can affect their metabolic profiles. • Drugs given too frequently may overload the metabolic system available to it, leading to elevated blood and tissue levels of the drugs. The effect of protein binding also influences the metabolism Drug interactions • Phenobarbital stimulate the metabolism of Diphenylhydantoin. • The half life of Chloropropamide, Diphenylhydantoin & Cyclophosphamide is increase in presence of Chloramphenicol. • Plasma Concentration of anticoagulants such as Warfarin are reduced by simultaneous application of barbiturate Phase I (Functionalization reactions • Oxidations (electron removal, dehydrogenation and hydroxylation) • Reduction ( electron donation, hydrogenation and removal of oxygen ) • Hydrolytic reactions of amide & ester. Oxidation Reactions • The main enzymes involved in the oxidation of xenobiotics called mixed – function oxidases or monooxygenases, found mainly in the liver but also occur to less extent in other tissues. • Cytochrom P-450 ( CYP – 450 ) Simplified Cytochrome P450 Redox Cycle Major reactions of oxygenation catalyzed by cytochrome P450: 1-Carbone oxidation reaction: 2-N-Oxygenation reactions. a)Hydroxylation of Saturated aliphatic C atom. b)Hydroxylation of aromatic ring. c)Oxidation of unsaturated aliphatic system. Major reactions of oxygenation catalyzed by cytochrome P450 Oxidation reactions 1. Carbon oxidation reaction abcd- Hydroxylation of saturated aliphatic carbon atoms Hydroxylation at activated SP3 carbon atoms Oxidation attack on unsaturated aliphatic systems Hydroxylation of aromatic rings 2. N-oxygenation reactions 3. S-oxidation reactions Hydroxylation of saturated aliphatic carbon atoms • Saturated aliphatic C-H bonds are normally metabolised by hydroxylation ( ω & ω-1 ) Enzymatic introduction of a hydroxyl group into cyclohexane ring generally occurs at C-3 or C-4 In human the trans-4-hydroxycyclohexyl product has been reported as a major metabolite of acetohexamide ( hypoglycemic agent ) Terodiline Aromatic p-hydroxylation predominate with Risomer where as benzylic hydroxylation is preferred with S-isomer. Hydroxylation at activated SP3 carbon atoms Oxidation involving carbo-heteroatom system: N,O,S func.gp are commonly found in most drug &foreign comp. metabolic oxid. of C-N & C-S involve hydroxylation of alpha carbone atom attached directly to heteroatom(N,O,S) N-dealkylation: oxidative alpha-hydroxylation at alpha-C then dealkylation. Halogenated aliphatic derivatives Oxidation attack on unsaturated aliphatic systems (alkene epoxidation).