* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 3 Biochemistry with notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
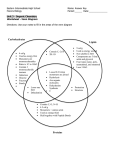
Chapter 3 BIOCHEMISTRY 3-1: Carbon Compounds • Who’s made of them??? Organic Compounds Vs. Inorganic • Carbon, carbon, carbon! • Living organisms...mostly __________ – Almost everything else is _________! • No carbon CARBON • # valence electrons? • Wants to bond to • Forms: What are the “lines”? • Each C forms HOW MANY bonds? Single, Dbl, Tpl FUNCTIONAL GROUPS • Clusters of • Hydroxyl groups • Soluble in Making Large Carbon Molecules: “MACROMOLECULES” • MONOMER: • POLYMER: How’s It Work? • Condensation Reactions Figure 3.4 Condensation of Polymers : Water is removed; Cov bond forms b/w monomers • In words... • WATER comes from • Monomers? Polymer? MMMMM.Tasty. Gotta break it down. HOW? • Reactions • REVERSE of • is USED to break bonds Figure 3.4 Hydrolysis of Polymers– water is added; cov bond b/w monomers is broken ACT IT OUT! • You’re lots of monomers • One by one you link up..... “??? reactions?” • Now you’re a .... “???” • Now one by one you break up... “??? Reactions?” • Now you’re “???” ATP •A t p • 3 “parts”: • Phosphates joined by • Break releases • reaction http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/60028.htm Page 54: 1-3, 5-7, 10 3-2: Organic Compounds What is an organic compound??? • Compounds made up of ... • C, H, O Proteins • Monomers: Amino Acids, peptide bonded together • C,H,O, N & Sometimes S • Major use? – Structural (keratin) – Functional (enzymes, hemoglobin) http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/60044.htm Amino Acids • (monomers for proteins) • basic structure – Central carbon atom – A single Hydrogen atom – A Carboxyl group – An amino group – R group R group Peptide Bonds • Special covalent bond – condensation reaction Amino Acids • 20 different ones used by human body • Body produces most – not all; not in great enough quantities • Two categories – Essential - must be obtained by food – Non-essential - produced by human body Amino Acids in Food • plants and seeds • Animal products – Ex. Eggs, milk, fish, poultry, and beef 1 type of Protein: Enzymes •Biological catalysts •ESSENTIAL FOR CELL FUNCTION!!! •Substrate(s) fits @ active site(s) •Reaction occurs here product(s) Draw it!! Enzymes http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/60034.htm Fast Food Math Lipids • C,H,O & Non-polar – NOT soluble in water • Examples include… – Fats-- Triglycerides – Oils – Waxes • Uses: – Cell membranes--phospholipids – Steroid hormones http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/60035.htm Lipids...more uses • Excess fats stored by the body – Under skin for warmth – Around organs for protection • Long-term (stored) source of energy!!! Lipids • Monomers: glycerol & fatty acids • Diff Structures: – Saturated • all C atoms connected with single bonds – Unsaturated • At least one C bond is a double bond – Polyunsaturated • Two or more bonds are double Ex: phospholipids, butter, oils Carbohydrates • Monomer: sugar • C,H,O in 1:2:1 ratio • Short-term source of energy – (cell respiration) – Sugars are quickly converted to ATP • Usable energy Carbohydrates • Three types of sugars – Monosaccharides Ex: Ex: glucose, glucose, glycogen, glycogen, sucrose sucrose • Simple, one sugar – Disaccharides • Two chemically bonded monosaccharides – Polysaccharides • Complex, made up of many monosaccharides • Requires use of enzyme to break down to useable form http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/60029.htm Nucleic Acids • 2 examples/types: • DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid • RNA – Ribonucleic acid http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/60041.htm For both: • Monomer: Nucleotide – Three parts • Phosphate group • Five-carbon sugar • Ring shaped nitrogenous base p. 60 #1-5, 7, 8, 10 Pineapple Enzyme Lab Prediction Table Name Which cup Why? Pineapple Enzyme Lab Data Table Cup Jello only Jello+Fresh Jello+Canned Qualitative observations Pineapple enzyme lab PROCEDURE: • Label all cups with your period & team name and label them: FRESH, CANNED, PLAIN • Make Jello according to instructions on box. • Put one piece of canned pineapple in the “CANNED” cup. • Put one piece of fresh pineapple into the “FRESH” cup. • Carefully pour 15mL of Jello into each of your three cups • MEASURE CAREFULLY, THIS IS AN EXPERIMENT!! • Refrigerate overnight. Make qualitative observations tomorrow. • CLEAN UP YOUR LAB AREA!!! – You will lose points if you leave it a mess