* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mixtures & Organic Compounds
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
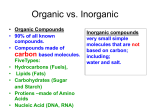
CHAPTER 2 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Level of organisation ATOM MOLECULE ELEMENT COMPOUND SOLUTION Water Only 4 of the 90 elements make up more than 96% of the mass of the human body. They are: Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) Nitrogen (N) Mixture and Solutions When elements combine to form a compound, the elements no longer have their original properties. A mixture is a combination of substance in which the individual components retain their properties. Ex: Sand and sugar A solution is mixture in which one or more substances (solute) are distributed evenly in another substance (solvent). Ex: Kool-aid *The concentration of solute is important to organisms A suspension is a mixture of water and nondissolved materials Acids and Bases Chemical reactions can occur only when conditions are right; they depend on the pH of the environment pH is a measure of how acid or basic (alkaline) a solution is A scale with values ranging from 0 to 14 is used to measure pH H+ OH- ACID is any substance that forms hydrogen ions (H+) in water. Ex: HCl (H+) and (Cl-) has a pH of below 7 BASE is any substance that forms hydroxide ions (OH-) in water. Ex: NaOH (Na+) & (OH-) has a pH above 7 Buffers=dissolved compounds that control pH in the body ( HOMEOSTASIS) Buffers are weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp sudden changes in pH. Importance of Acids and Bases to Biological Systems Chemical reactions in organisms depend on the pH of the environment Ex: Pepsidase is an enzyme that works best in the acidic human stomach Organism A__________ Organism B --------------4.5 10.5 0-8 0 1 2 3 4 5 6.5-14 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Certain organisms require a certain pH environment for optimum (best) growth 14 Life Substances 1.Organic compounds are derived from living things and contain Carbon, must have Carbon and Hydrogen to be organic 2.Inorganic compounds are derived from nonliving things (ex: Water, Carbon Dioxide) Carbon compounds: easily form 4 covalent bonds to create chains , rings, or branches •Polymerization: when a large compound (polymer) is produced from smaller compounds (monomers) as the smaller compounds are joined together. •Macromolecules: large polymers Condensation Reaction (dehydration synthesis) to make or build, water is produced Hydrolysis to split, water is added 1.Carbohydrates 2.Lipids 3.Proteins 4.Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Composed of C (Carbon), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) in approximate ratio 1:2:1 Monosaccharide: single (simple) sugar Molecular formula for all 3: C6H12O6 GLUCOSE-Produced by plants through photosynthesis FRUCTOSE-found in fruits GALACTOSE-found in milk Disaccharides formed by 2 sugars C12H22O11 Sucrose = glucose + Fructose Maltose = glucose + Glucose Lactose = glucose + Galactose Polysaccharides formed by more than 2 sugars Starch-storage for plants Glycogen-storage for animals (liver) Cellulose-cell wall of plants Chitin=cell wall of fungi What makes them different from one another is the arrangement of the individual atoms (structural formulas) Isomers – compounds that differ in structure but nor in molecular composition Synthesis of Dissachharides Glucose + Fructose Sucrose + C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 + Water + H2O + C12H22O6 * Dehydration synthesis-water is squeezed out Hydrolysis of Disaccharide Sucrose + Water Glucose + C12H22O6 + Fructose + + H2O C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 * Hydrolysis-water is added Lipids: Fatty Compounds Made of C, H, O w/ a greater # in C:H atoms and a smaller # of O atoms than carbohydrates (No uniform Ratio) Ex: fats, oils, waxes (do Not dissolve in water) Many common lipids are constructed of a unit of: •Glycerol (3-Carbon Alcohol) combined by dehydration synthesis •3 fatty acids-hydrocarbon chain with an Carboxyl Group -COOH 3 fatty acids-hydrocarbon chain with an Carboxyl Group -COOH Hydrophilic End (water loving-carboxyl end that is polar) Hydrophobic End (water fearinghydrocarbon end that is nonpolar) Functions: forms much of cell membrane to serve as a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell – energy storage for cells Ex: waxes, triglycerides Proteins: Organic Compounds made of C, H, O, N Polymer made of amino acids (monomers); organisms have thousands of proteins Amino Acids: 20 different kinds that form proteins-has 5 Groups: a) Central C atom b) Single H atom c) Carboxyl Group (COOH) d) Amine Group (NH2) e) R Group (repeating CH2 + CH2 of different lengths) Dipeptide: 2 amino acids bound together covalently by condensation reaction (a molecule of H2O is lost)held together by peptide bonds b) a) d) c) e) Amino acid Amino acid Water Dipeptide Polypeptide: A long chain of amino acids held together by peptide bonds Ex of Proteins: Insulin (hormone), hemoglobin, and enzymes Nucleic Acids: complex organic molecules that store important information in the cell 2 important types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA 1.DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): stores essential info for almost all cell activities-including cell division 2.RNA (ribonucleic acid): stores and transfers info for proteins Nucleotides: monomers that make up both DNA & RNA-made up of 3 main components: Phosphate Group Five-Carbon Sugar Nitrogen Base (ring)