* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.2_Organic_Compounds ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
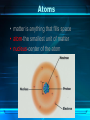
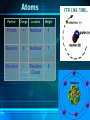
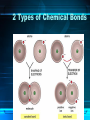
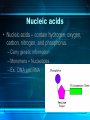
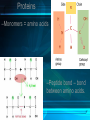
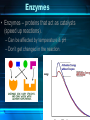
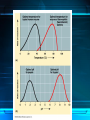
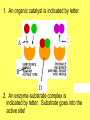
The Chemistry of Life Chapter 2 Atoms • matter is anything that fills space • atom-the smallest unit of matter • nucleus-center of the atom Atoms Particle Charge Location Weight Proton + Nucleus 1 Neutron 0 Nucleus 1 Electron - Electron Cloud 0 2-1 Atoms 6 C Carbon 12.011 Atomic Number = # of protons (or electrons) Symbol Name Average Atomic Mass = protons + neutrons 2-1 • element-pure substance that consists of one type of atom Isotopes • Isotopes – atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons. – Ex: C-12, C-13, and C-14 2-1 Chemical Compounds • Compound – a substance formed by the chemical combination of two more elements. – Example: H20, NaCl 2-1 2 Types of Chemical Bonds Covalent Bonds • A covalent bond forms when two atoms share electrons – Forms molecules like water water (H20) Ionic Bonds • When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes electrically charged • Charged atoms are called ions • Ionic bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions The Water Molecule • Polar molecule – has a positive and negative end because electrons aren’t shared evenly. •Allows it to form hydrogen bonds Solutions • Solution – mixture in which all components are evenly distributed. – Solvent – does the dissolving (water) – Solute – gets dissolved (Kool-Aid) 2-2 H2O-->H+ & OH• = Hydrogen ion • in excess= acid • OH = Hydroxide ion • in excess= base + H Acids, Bases, and pH • pH scale– measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14 Acids, Bases, and pH • Acids – form H+ ions in solution, pH less than 7. (ex: stomach acid) • Bases – form OH- ions in solution, pH greater than 7. (ex: oven cleaner) • Buffers – chemicals that prevent sudden changes in pH. 2-2 Carbon! • Organic compounds – contain carbon and are associated with living things. www.nerdscience.com 2-3 Organic Polymers • Polymers – macromolecules made of repeating units called monomers. • Four types: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins. Monomers Polymer 2-3 Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates – compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio usually 1 : 2 : 1. – Energy source!!! – Ex: sugars, starches, glycogen, cellulose – Monosaccharides (monomer) (glucose) – Polysaccharides (polymer) (starch) 2-3 Carbohydrates Lipids • Lipids – made of mostly carbon and hydrogen atoms. – Fats, oils, waxes – Three fatty acids and a glycerol – Store energy, make membranes, waterproof 2-3 Lipids Nucleic acids • Nucleic acids – contain hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. – Carry genetic information – Monomers = Nucleotides – Ex: DNA and RNA 2-3 Proteins • Proteins – contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. – Form bones/muscles, transport substances, fight disease, control reactions, regulate cell processes. 2-3 Proteins –Monomers = amino acids –Peptide bond – bond between amino acids. Chemical Reactions • chemical reaction: a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 Reactants Products CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 Reactants Products Enzymes • Enzymes – proteins that act as catalysts (speed up reactions). – Can be affected by temperature & pH – Don’t get changed in the reaction. 2-4 Enzymes 1. An organic catalyst is indicated by letter A C B D 2. An enzyme-substrate complex is indicated by letter. Substrate goes into the active site!