* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Compounds
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
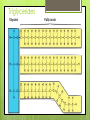
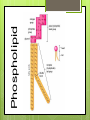
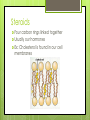
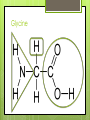
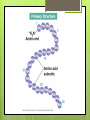
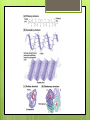
Organic Compounds Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins & Nucleic Acids Carbon Why is carbon so special? Atomic # 6 4 valence electrons Can make up to 4 covalent bonds Building block for the biomolecules of life! Macromolecules 4 Macromolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Protein Nucleic Acids People Love Chicken Nuggets Macromolecules Every macromolecule has Monomer Single unit of a whole Polymer Many units or monomers bonded together Carbohydrates Made of carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen Unique 1:2:1 pattern Used for energy mostly and sometimes for structure in plants Monomer: monosaccharide 2 monomers: disaccharide Polymer: polysaccharide Units of Carbs There Glucose – our energy source Fructose - sweetner Galactose – not as common There are 3 monosaccharides are 3 polysaccharides Glycogen – how we store carbs Starch – how plants store carbs Cellulose – structure in plants Lipids Made of carbon & hydrogen Does not dissolve in water High ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms Four types of lipids Fats Oils Waxes Triglycerides Triglycerides - FATS Saturated Have no double bonds in their fatty acid chains – maximum # of H atoms Straight Fat chain Usually animal fats Solid at room temperature Triglycerides – OILS Unsaturated Have at least one double bond in their fatty acid chain Forms Fat a kink in the chain Usually oils and from plants Liquid at room temperature Phospholipid Phospholipid Found in all our cells Makes up the cell membrane 2 layers of phospholipids lipid bilayer Phospholipid Bilayer Wax One fatty acid chain to a glycerol Waterproof Create protective layer in animals and plants Steroids - hormones Steroids Four carbon rings linked together Usually our hormones Ex: Cholesterol is found in our cell membranes http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/obesi ty/obesity_molecular/01.html http://www.wisconline.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID= AP13204 Protein Macromolecules with carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen Monomer: amino acid 2 monomers: dipeptide Polymer: polypeptide Amino Acids Each amino acid has three main groups Amino group Carboxyl group R group (changes) Change the formation and properties of the amino acid Amino Acid Glycine R group The R group makes each amino acid different There are 20 possible amino acids based off this one group The R group is = variable Proteins Peptide bond = covalent bond Links amino acids together For every peptide bond, one molecule of water is formed Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=va0D NJId_CM Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lijQ3a 8yUYQ Enzymes Proteins are in our bodies everywhere! Enzyme is a type of protein that is a catalyst Catalyst starts a reaction Produce proteins Enzymes Each enzyme has an area known as the active site Where a specific molecule binds and a reaction occurs The molecule binding is called a substrate Enzyme conditions Enzymes work at a specific conditions Temperature pH Causes enzyme to change shape and lose its function http://www.sumanasinc.com/webconten t/animations/content/proteinstructure.ht ml Nucleic Acids Contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus Nucleic Acids Monomer = nucleotide 5 carbon sugar Phosphorous group Nitrogenous base Properties Store genetic information Two kinds of nucleic acids DNA RNA Fold it! Help scientists figure out protein folding This game is open to the public The first hundred puzzles are known proteins But many proteins are not decoded and scientists are asking for our help to figure them out http://fold.it/