* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
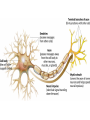
Download Motor neurons
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorders and memory wikipedia , lookup
Test anxiety wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Antidepressant wikipedia , lookup
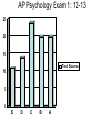
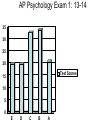
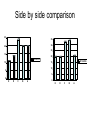
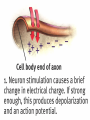
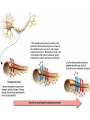
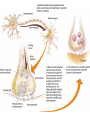
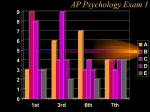
AP Psychology Exam 1: 12-13 25 20 15 Test Scores 10 5 0 E D C B A AP Psychology Exam 1: 13-14 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Test Scores Side by side comparison 25 35 30 20 25 15 20 2012-2013 10 2013-2014 15 10 5 5 0 E D C B A 0 E D C B A Stats: Unit 1 Exam • 100% of students who came on his or her own time to ask questions earned a B or higher on the test – What is the extraneous variable here? Is this cause/effect? • 94.6% of students who got 7/7 for RQ earned a B or higher on the test • 98.7% of students who failed RQ earned a D or lower on the test – What correlations can you make? Are they positive or negative? • How will you personally be able to work against the extraneous variable from the first bullet if you were not successful on this test? Where do we go from here… • Let’s make a deal… 1. Conference 2. Study 3. Improve • Drop this test if improved by 2 letter grades (or B to an A) most missed questions A negative correlation between degree of wealth and likelihood of suffering from a psychological disorder would indicate that a. b. c. d. e. Poverty makes people vulnerable to psychological disorders The poor are more likely to have a psychological disorder than the wealthy Psychological disorders usually prevent people from accumulating wealth Poverty causes vulnerability to psychological disorders All the above are true Cont’d Alexandra is told that research supports the value of cosmetic surgery for boosting self-esteem. Belinda is told that the esteem-enhancing value of cosmetic surgery has been refuted by research. Both women would consider the findings to be common sense. This best illustrates the power of a. b. c. d. e. Random sampling The false consensus effect The hindsight bias Illusory correlation Confirmation bias Neurons: • Sensory neurons - afferent • Motor neurons - efferent • Interneurons The Neuron: the basic building block (cell) of the nervous system. • Neurons are composed of the following parts: – Axon – Soma/Cell Body – Dendrite – Myelin sheath – Terminal Branches – Terminal Buttons – Synapse – Post synaptic Dendrite – Glial cells Neuron Parts continued –Synapse-space between neurons. • Aka Synaptic Gap/Cleft or Nodes of Ranvier –Action Potential- electrical charge that runs through the neuron caused by depolarization of the neuron. All or None Law: Like firing a gun • Neuron will fire or it won’t – there is no between – Squeezing a trigger hard or soft? – Turning on a light switch slow or fast? Neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters can be excitatory or inhibitory: – Agonists excite, – Antagonists inhibit • Endorphins block • Heroin tolerance and withdrawal \ Acetylcholine (ACh) • Released by motor neurons • Regulation of attention, arousal, and memory • Enables muscle action, memory and learning • Lack of Ach creating neurons = Alzheimer’s Dopamine (DA) • Control of voluntary movement • Cocaine and amphetamines elevate activity at DA synapses • “reward pathway” • Too little = Parkinson’s • Too much = Schizophrenic disorders, addictive disorders Norepinephrine (NE) • Mood and arousal • Cocaine and amphetamines elevate activity at NE synapses • Too little = depression Serotonin • Regulation of sleep and wakefulness, aggression • Prozac and antidepressant drugs affect serotonin circuits • Too little = depressive disorders GABA or gamma-aminobutryic acid • Inhibitory transmitter • Regulates anxiety, sleep/arousal • Too little = insomnia, anxiety disorders Glutamate • Widely distributed excitatory transmitter • Learning and memory • Too much = migraines or seizures – Why do people avoid MSG? Endorphins • • • • Resembles opiates in structure and effects Roles in pain relief and response to stress Regulation of eating behavior “Runner’s High” Monoamines • 3 neurotransmitters – Dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin GABA and Glutumate • Consist of amino acids – GABA - produces only inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (PSP) – Glutamate – widely distributed in the brain, only has excitatory effects MAOI’s • Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor • Antidepressants used to treat depression, anxiety, etc SSRI Antidepressants • Selective Serotonin Re-uptake Inhibitor • Anti depressant drugs (and some other illegal drugs like cocaine) – block the reuptake of neurotransmitters, keeping in the synapse longer, – intensifying their activity. – For some depressed people that elevates their mood. Opiod peptides and Substance P • Among those peptides known to affect synaptic transmission are substance P and the opioid peptides. • The best-studied are the opioid peptides, so called because opiate drugs, such as morphine, are known to bind to their receptors and mimic their painkilling and mood-altering actions. END OF DAY 1