* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (DNA) and ribose (RNA)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
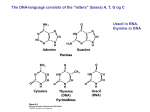
The DNA-language consists of the ”letters” (bases) A, T, G og C Uracil in RNA, thymine in DNA The bases in DNA (A) and RNA (B) are coupled to each other via deoxyribose (DNA) and ribose (RNA), and with phosphate A B The structure of DNA (one strand shown) and RNA Note that the strands are antiparallel and have a 5’ (5-merket) and a 3’ (3-merket) ende Most DNA molecules are right-handed twisted DNA-molecules can be visualized by elektron microscopy, here illustrated by a particularly small molecule (plasmid, see later) DNA can replicate itself by the help of numerous proteins. This is perhaps the most important characteristic of life! Life anywhere (in the universe!) without copying is difficult to envision Proteins consist 20 different amino acids (R varies) Covalent sulfur bridges can occur in proteins. This can have a major effect on protein 3D structures and therebye functionality The acid-base properties of amino acids have a big effect on protein functionality The amino acids in proteins are held together by covalent peptide bonds. Note that this defines the carboxyterminal and amino-terminal ends of proteins. Polymerization occurs such that the amino acid at the amino terminal end is the first to become incorporated. The penta-peptide Ser-Gly-Tyr-Ala-Leu (SGYAL) Monosaccharides are aldoses or ketoses Many monosaccharides are epimers of each other The monosaccharides can (and will) also be found in ring form Monosaccharides can be linked to each other and become carbohydrate storages (starch) or have structural functions (cellulose, chitin etc.) The stiff ”skeleton” of this insect contains a lot of chitin, also in shrimps, crabs etc Fungi can ”eat” the cellulose, which is a major component of wood. Cotton is almost pure cellulose. What would happen if no organism could utilize cellulose (like humans)? Lipids typically have long chains of carbon atoms, but exist in many forms, also linked to polysaccharides (lipopolysacchariders), phosphate (phospholipids) and as triglycerides. They are typically found in cell membranes and as stored fat (do you see it on yourself?). Candle-lights are composed of long chain fatty acids Different triglycerides (note the double bonds, which are interesting in relation to human health) Central Dogma genetic information in DNA is passed to next generation (heredity) DNA storage of genetic information RNA carrier of genetic information Proteins carry out the functions of the cell This is probably the most important of all slides in the course! An alternative way of illustrating the central dogma