* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 2
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Natural product wikipedia , lookup
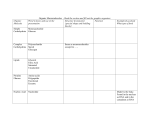
Atom Building block of life (MOLECULES/COMPOUNDS) Atom Building block of life (MOLECULES/COMPOUNDS) A atom CARBON MOLECULE 2 or more atoms bonded together MOLECULE 2 or more atoms bonded together O2 ORGANIC A chemical compound containing carbon and relating to living organisms. ORGANIC A chemical compound containing carbon and relating to living organisms. ORGANIC A chemical compound containing carbon and relating to living organisms. BIOMOLECULES Molecules containing the substances that are necessary for performing life functions. BIOMOLECULES Molecules containing the substances that are necessary for performing life functions. BIOMOLECULES Molecules containing the substances that are necessary for performing life functions. CARBOHYDRATE • A biomolecule containing hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio CARBOHYDRATE • A biomolecule containing hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Proteins • A biomolecule composed of amino acids connected by peptide bonds. Proteins • A biomolecule composed of amino acids connected by peptide bonds. AMINO ACID • Molecule that contains an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, and a side chain specific to each amino acid. AMINO ACID • Molecule that contains an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, and a side chain specific to each amino acid. AMINO ACID • Molecule that contains an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, and a side chain specific to each amino acid. POLYMER • Large MOLECULE formed by bonding of smaller MOLECULAR UNITS. GLUCOSE Simple carbohydrate, supplies QUICK ENERGY SUGAR = ENERGY GLUCOSE Simple carbohydrate, supplies QUICK ENERGY SUGAR = ENERGY GLUCOSE Simple carbohydrate, supplies QUICK ENERGY SUGAR = ENERGY MONOSACCHARIDE Building block (monomer) of a carbohydrate MONOSACCHARIDE Building block (monomer) of a carbohydrate Monomer of Carbohydrate FATTY ACID • Building block (monomer) of a lipid FATTY ACID • Building block (monomer) of a lipid • Monomer of LIPID Hydrophobic • FEAR OF WATER (substance does not react with water) Hydrophobic • FEAR OF WATER (substance does not react with water) • PROPERTY (description) Hydrophobic • FEAR OF WATER (substance does not react with water) LIPID • A biomolecule composed of glycerol and fatty acids that is hydrophobic….. LIPID • A biomolecule composed of glycerol and fatty acids that is hydrophobic….. LIPID • A biomolecule composed of glycerol and fatty acids that is hydrophobic….. Hydrophilic • WATER LOVING • A substance that reacts with water • PROPERTY (description) Hydrophilic • WATER LOVING • A substance that reacts with water Hydrophilic • WATER LOVING • A substance that reacts with water MONOMER • A small molecular unit that can be chemically combined with other small molecular units to form a large molecule Dehydration Synthesis • The chemical process in which water molecules are released to form bonds between monomers to produce polymers • Mnemonic (when you sweat = water released and then you get dehydrated) Hydrolysis • CHEMICAL PROCESS = In which water molecules are added to break the bonds of a polymer Metabolism • All of the physical and chemical processes that occur within an organism Metabolism • All of the physical and chemical processes that occur within an organism Metabolism • All of the physical and chemical processes that occur within an organism Products The substances resulting from a chemical reaction Products The substances resulting from a chemical reaction Flour + Eggs CAKE Products The substances resulting from a chemical reaction Flour + Eggs CAKE Products The substances resulting from a chemical reaction Flour + Eggs CAKE REACTANTS • Any substance that undergoes chemical change REACTANTS • Any substance that undergoes chemical change Flour + Eggs CAKE REACTANTS • Any substance that undergoes chemical change Flour + Eggs CAKE REACTANTS • Any substance that undergoes chemical change Flour + Eggs CAKE