* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GEOL 1130 Nutrient Cycles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
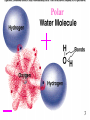
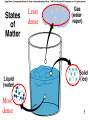
Nutrient Cycles • • • • • • The magic of water What is a Nutrient? The Carbon cycle The Nitrogen cycle The Phosphorus cycle The Sulfur cycle 1 The Magic of Water • Life is watery! – 60-70% by weight of living organisms • Makes possible chemical reactions necessary for life • Promotes neutrality 2 Polar 3 3 Extra OH- H+ + OH- = H2O Extra H+ CS Fig. 3.4 4 4 Least dense Most dense 55 The Magic of Water • Life is watery! • Makes possible chemical reactions necessary for life Polarity • Promotes neutrality • Sticks together • Holds heat • Large liquid temperature range • Ice Floats! • Evaporation provides cooling mechanism for organisms – Did you remember your deodorant today? 6 What are Nutrients? • Elements used as building blocks in organic compounds needed to build living cells • C. HOPKINS More basic than vitamins! These are the things vitamins are made of 7 C H O 88 Similar to CS Fig. 3.12 9 9 CS Fig. 3.13 10 10 Energy transfer in sample ecosystem Fig. 3.16 11 Biomass (with nutrients) transfer Fig. 3.17 12 Fig. 6.2 Biogeochemical Cycles = Natural + Anthropogenic ANTHROPOGENIC = HUMAN ORIGIN 13 SHORT TERM BIOTA ATMOSPHERE 14 14 Years to Millenia LONG-TERM Atmosphere Millions to CS Fig. 100’s of 3.15 Millions Biota Ocean Crust CS Fig. 3.20 15 15 Carbon Cycle (petagrams = 1015 grams) Natural sources = 207 Anthropogenic sources = 6.4 – 7.4 Natural removals = 210 16 Similar to CS Fig. 3.20 Nitrogen • Main reservoir is N2 in atmosphere – Cannot be used directly by plants • Necessary to build amino acids, peptides, proteins • DNA! 17 ATMOSPHERE ! BIOTA 18 18 Nitrogen made available for Life • N2 -> NO2- -> NO3- -> NH4+ -> Peptides and Proteins Or in words: • Gas – Nitrite – Nitrate – ammonium – organic molecules 19 Case Study: Why trees need salmon; pg 52 • Bears feasting on salmon leave about half of carcass in woods – Scavengers and bears deposit up to 120 kg of N/hectare • Similar to fertilizer quantities added to forest plantations • Nitrogen important nutrient for trees – In good salmon years, rainforest trees grow up to three times as fast • Forest ecosystem needs stream ecosystem and stream ecosystem needs forest ecosystems – Implications for salmon management? Most stocks down 90% and some gone 20 Nitrogen Cycle (teragrams = 1012 grams) Anthropogenic = 170 - 445 Natural = 196 - 733 Eutrophication = The addition of excess nutrients to natural waters 21 Similar to CS Fig. 3.21 Phosphorus • P necessary for – Nucleic acids – Cell membranes – Energy-transfer reactions – Bones – Teeth • Source: Minerals (soil) 22 CRUST BIOTA 23 23 NATURAL CYCLE BIOTA OCEAN CRUST 24 CS Fig. 3.23 Phosphorus laid down as fertilizer more than what is delivered through Erosion!! 25 Island of Nauru after mining for phosphorus 26 Sulfur • S important for proteins • Source: Minerals (soil) 27 Sulfur Cycle in 1012 moles Anthropogenic = Significant! Causes Acid Rain 28 Similar to CS Fig. 3.24 The End. Back 29