* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cortical stimulation mapping wikipedia , lookup
Neurodegeneration wikipedia , lookup
Lumbar puncture wikipedia , lookup
Brain damage wikipedia , lookup
Hemiparesis wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
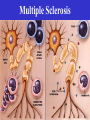
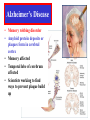
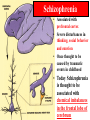
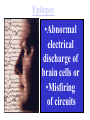
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome What are the 2 main differences you see?? Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Sometimes you can tell, sometimes you can’t! FAS website: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome • FAS stunted growth and distinct facial features • Brain damage resulting in difficulty learning and inability to recognize cause and effect (difficulty knowing right from wrong). • Depending on when damage occurred during pregnancy: Heart Murmur, Spina bifida, Hydrocepalus, Eye, liver and kidney problems, fetal tumors ADHD • • • • • • Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder Dopamine thought to be reabsorbed too quickly It does not spend enough time in the synapse Ritalin : increases dopamine & norepinephrine Ritalin also known as methylphenidate Long term effects unknown! Multiple Sclerosis • An acquired inflammatory, demyelinating disease of the CNS • Cells of the immune system invade the CNS and destroy myelin • It strikes people in the prime of their lives, usually between 20 and 40 years of age • Both genetic and environmental factors have been implicated in the disease. Multiple Sclerosis Brain Web: Diseases Autism • Abnormalities in brain • Some studies suggest abnormality exists in specific protein responsible for re-uptake of serotonin • Other studies indicate problem with receptor for GABA (gamma amino butyric acid) • Brain’s chemical message system not functioning properly Parkinson’s Disease • • • • • Progressive degeneration of midbrain Midbrain loses it’s ability to produce dopamine Dopamine is an opiate-like neurotransmitter Dopamine produces feelings of well being Results in muscular tremors, partial facial paralysis and general weakness • L-dopa given to slow • Watch movie “Awakenings” with Robin Williams Alzheimer’s Disease • Memory robbing disorder • Amyloid protein deposits or plaques form in cerebral cortex • Memory affected • Temporal lobe of cerebrum affected • Scientists working to find ways to prevent plaque build up Schizophrenia • Associated with prefrontal cortex • Severe disturbances in thinking, social behavior and emotion • Once thought to be caused by traumatic events in childhood • Today Schizophrenia is thought to be associated with chemical imbalances in the frontal lobe of cerebrum Spinal Cord Injuries • Spinal cord may be damaged by disease or injury • If spinal neurons in cervical area damaged: result is complete paralysis • This is known as quadriplegia • If spinal neurons in lower back (lumbar area) are damaged: paraplegia Hydrocephalus • Water on the brain • Caused by build up of csf due to over production or inability to drain excess csf • Pressure builds up and squeezes brain against skull • Reduced brain mass and intelligence results • Shunt may be implanted to drain csf Spina Bifida Permanently disabling birth defect. Spine does not close properly in first month. Spinal cord may protrude through the back Cerebral Palsy • Caused by insufficient supply of oxygen to the fetus • Possibly occurring during birth process • Result is reduced or lack of muscle coordination • Brains are perfectly normal in terms of learning capabilities Encephalitis • Inflammation of the brain • Usually caused by virus or bacteria • Encephalitis lethargica (or sleeping sickness) is an example • Person feels apathetic, has double vision and extreme weakness Japanese encephalitis Virus transmitted by mosquito Leads to paralysis, seizures and coma Meningitis • Inflammation of membranes surrounding brain and spinal cord • Usually caused by virus or bacteria • Person has cold symptoms initially then becomes increasingly ill • Membranes inflamed include Dura mater, Arachnoid and Pia mater (outer, middle and inner meninges) Epilepsy •Abnormal electrical discharge of brain cells or •Misfiring of circuits Epilepsy • Nervous system disorder that produces sudden, intense bursts of electrical activity in the brain. • This abnormal electrical activity in the brain causes seizures – which may briefly upset a person's muscle control, movement, speech, vision, or awareness. Kuru • Noticed in New Guinea in early 1900s • Women of the region were responsible for preparing the corpse of those who died – often ate brain matter, fed it to children and elderly • Eight times more women than men contracted kuru Kuru • Disease has three stages: – Ambulant: • Individual can still walk, but is uncoordinated, has slurred speech. – Sedentary (AKA Laughing Stage) • Can’t walk on their own, have tremors and jerkiness • Extreme emotions – laughing and crying. – Terminal • Cannot sit up on their own • Urinary & fecal incontinence • Sounds like affect of alcohol.