* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecular Representations - West Chester University of
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
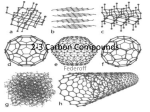
The World of the Cell Wayne M. Becker Lewis J. Kleinsmith Jeff Hardin Gregory Paul Bertoni Seventh Edition Chapter 2 The Chemistry of the Cell Pages 18-40 Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. Five Principles The Importance of: 1. Carbon 2. Water 3. Selectively Permeable Membranes 4. Synthesis by Polymerization of Small Molecules 5. Self-Assembly Nature of Phospholipids -Amphipathic molecules Structure of Phospholipids -Polar Head Groups -Nonpolar tails Lipid Bilayer What defines the specific function of a membrane? Major Intracellular Compartments Membrane Structure -Different Regions -Protein Function -Sugars -Others Protein Channel Types Macromolecules • Important Theme: – Small molecular repeat units “condense” to form macromolecules – Macromolecules “self-organize” to mature biological dstructure – Repeat Units - “monomers” – Repeat Units condense: • • • • 2 repeat units - “dimer” 3 repeat units - “trimer” Several repeats units - “oligomer” Many repeat units - “polymer” Assembly of Cellular Structures Families of Macromolecules Macromolecule Formation Monomers condense - water is released - Condensation often releases water -“Dehydration condensation” Reverse = “degradation” – Water is added – “Hydrolysis” Simple Sugar Structure Glucose Formation of a Disaccharide Which reaction requires energy? Monomers Polymers Macromolecules • Recurring Theme… • Monomers condense to polymers.. • Polymers “self-organize” into mature macromolecules.. Self Assembly • Polymers must assume exact final 3D shape and structure • How “molded” into final 3-D shape? • Biological “casting structure”? How do macromolecules assume their final 3-D shape? How do macromolecules assume their final 3-D shape? • Casting mold? Anfinsen Expt • 1920s • Functional Enzyme – “Pancreatic Ribonuclease” • “Denature” (disrupt 3D shape - usually only break non-covalent bonds) • Loose biological functionality Denaturation • Disrupt 3D structure (mainly through noncovalent bonds) • Leave sequence of condensed monomers intact.. Anfinsen Expt • Remove denaturation agent • Molecule spontaneously refolds to original 3D shape! • Biological functionality recovered.. Anfinsen Expt Means: – No “casting” mold necessary – All information needed to define 3D shape already present in “sequence” of amino acids – “3° structure is defined by 1° structure…” – How……? Defines 3D Structure: • “Non-Covelent” Bonds: – H-Bonds – Ionic bonds – VDW Bonds – “Hydrophobic” Bonds “Hydrophobic Interactions” UNFAVORABLE!! “Hydrophobic Interactions” Hydrophobic Interactions Hydrophilic – Water loving -can form hydrogen bonds -dissolve in water Hydrophobic – Water hating -cannot from hydrogen bonds -does not dissolve in water Hydrophobic force is caused by a pushing of nonpolar surfaces out of the hydrogen-bonded water network bringing nonpolar surfaces together Noncovalent Interactions of Macromolecules Final 3-D structure: • Final Trade-Off: – Maximize total number of favorable Noncovalent interactions – Minimize total number of unfavorable Noncovalent interactions