* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 30.2 Food and Nutrition - Faribault Public Schools
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Raw feeding wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Childhood obesity in Australia wikipedia , lookup
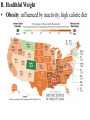
30.2 Food and Nutrition 1. Food and Energy A. Energy: • Cells use chemical NRG in food to make ATP (cell fuel) • ATP powers cell activities • Measure food NRG by burning: 1 calorie = heat needed to raise 1 gm H2O 1 ◦C • 1000 calories = 1 kilocalorie or 1 dietary Calorie B. Raw Materials: substances body needs (but can’t manufacture) to build/repair body tissues 2. Nutrients A. Water: most important – Cells need for proper chemical function – Dehydration: water loss greater than intake • Drink 1 liter fluids each day B. Carbohydrates: – Main NRG source – Simple/complex carbs converted to glucose • Cells metabolize to ATP for cell work – Glycogen: excess sugar stored in liver or converted to fat – Cellulose: plant fiber helps clean Dig. Sys C. Fats/Lipids • Help absorb fat-soluble vitamins • In cell membranes, nerves, hormones • Protect/insulate • Energy storage • Polyunsaturated (more than one double bond) • Trans fats: manufactures add H; solid at room temp; longer shelf life • Linked to heart disease D. Proteins: • Raw materials for growth/repair of body structures • Enzymes speed up body chemical reactions • Hormones: insulin regulates body sugar • Hemoglobins carries O2 in RBC”S E. Amino Acids: make up proteins • 8 essential AA: needed in diet F. Vitamins: need small doses; organic tools to build body components G. Minerals: inorganic nutrient molecules like Ca (bone health) and Fe (blood health) 3. Nutrition and Balanced Diet A. Balanced Diet: adequate nutrients and energy molecules to maintain health weight • Food labels: nutrition information • Fat: 9 C/gram (C-H bonds: harder to break releasing more energy) • Carb/Protein: 4 C/gram • % Daily Value/2000 cal. Diet • Age, gender, lifestyle affect need B. Healthful Weight • Obesity: influenced by inactivity; high calorie diet • Physical activity: burns excess calories; strengthens heart, bones, muscles • Amer. Heart Association: Diet w/30% Fat Max • 7% Saturated; 1% trans fats • Hi levels increase risk of heart disease & type II diabetes