* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diuretics & Antihypertensives
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
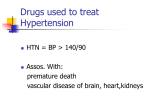
Chapter 20 Diuretics and Antihypertensives Diuretics and Antihypertensives p482 • Diuretics used to treat edema, ascites, HTN – Remove sodium and water from circulation • Antihypertensives: lower blood pressure • Both diuretics and antihypertensives – Used to treat hypertension (HTN) Classifications of diuretics p483 • Thiazide diuretics • Loop diuretics • Potassium-sparing diuretics • Osmotic diuretics • Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors • Combination potassium-sparing and hydrochlorothiazide diuretics Thiazide Diuretics p483 • Primary site of action – Renal distal convoluted tubule • Prevents sodium and chloride reabsorption into circulation – Prototype: hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) Thiazide Diuretics: Side Effects p483 • • • • • Loss of potassium Loss of sodium and chloride Hyperglycemia: high blood sugar Hyperuricemia: high uric acid Skin rash Thiazide Diuretics p483 • Safe • Require supplements – Potassium chloride • Administered as tablets, capsules, IV, liquids, and effervescent solutions • Teaching – Encourage the client to eat oranges, apricots, and bananas for K+ in diet – Signs/symptoms of hypokalemia, hyponatremia – Take diuretics in the morning for once a day dose. If twice a day dose, take second dose no later than 6pm. Loop Diuretics p485 • Prototype: furosemide (Lasix) – Works directly on the ascending limb of the loop of Henle • Inhibits sodium and chloride reabsorption – More potent than thiazides – Remain effective even in pt with seriously impaired glomerular filtration rates Loop Diuretics: Side Effects p485 • • • • • • Dry mouth Hypokalemia Hearing loss Fatigue Dehydration Hypotension Symptoms of hypokalemia p504 • Pulse irregularities, irregular HR • Leg cramps • General muscle weakness Symptoms of hyponatremia p503 • • • • • Weakness Confusion Abdominal cramps Muscle twitching If severe, seizures may occur Potassium-Sparing Diuretics p485 • Inhibit action of aldosterone (produced by adrenal cortex) or block Na+ reabsorption in distal tubule – Example: spironolactone, triamterene • Conserve potassium • Pt teaching: do not eat diet high in K+ Osmotic Diuretics p485 • Action: Produce a profound diuretic effect by a high concentration of osmotic agent in the kidney tubule. • Used to treat increased intracranial pressure and acute renal failure • Example – Mannitol Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors p485 • Examples: – acetazolamide – methazolamide • Very weak diuretic effect – Treats glaucoma: reduces the rate of production of aqueous humor in the eye Combination Potassium-Sparing and Hydrochlorothiazide Diuretics p 485 • Decreases adverse effects of each of the diuretic components – Decreases hypokalemia from thiazides – Decreases hyperkalemia from potassium-sparing diuretics • Examples: – Aldactazide • HCTZ and spironolactone – Dyazide • HCTZ and triamterene Hypertension p488 • An abnormal increase in arterial blood pressure Blood Pressure p488 • Blood pressure factors: CO = cardiac output PR = peripheral resistance • Normal blood pressure Systolic < 120 mm Hg Diastolic < 80 mm Hg Treatment for hypertension (HTN) p489 • Stepped care approach based on cardiovascular risk factors (box 20-1, 20-2, 20-3) • Lifestyle modification is always the first step in treating hypertension – – – – – Weight reduction Exercise program Smoking cessation Reduction of sodium in diet Moderation of alcohol intake Stepped care approach cont p489-490 • If lifestyle modifications do not achieve sufficient reduction in BP, then drug therapy is initiated. • Oral diuretics often first drug prescribed Central-Acting Antiadrenergics p490 • Potent antihypertensives. • Sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system is decreased • Epinephrine and norepinephrine is decreased • Adverse effect – Sedation • Example: clonidine, methyldopa – Short acting, must take multiple doses per day Central-Acting Antiadrenergics p490 • General side effect – High incidence of orthostatic hypotension • Instruct clients to change positions slowly • Sedation • Instruct clients – Do not stop meds abruptly • Rebound hypertensive crisis – Oral forms should be given with meals so that absorption is more gradual and effective. Peripherally Acting Antiadrenergic Agents p491 • Two main actions – Deplete norepinephrine • Adverse effect: depression – Block adrenergic receptors: Prevent sympathetic nervous system stimulation • Adverse effect: hypotension • First dose effect: development of significant hypotension and syncope with sudden loss of consciousness with the first few doses or if dosage is increased rapidly – Examples: • prazosin • terazosin • doxazosin Beta-adrenergic Blocking Agents “Beta blockers” p491 • Inhibit beta1 and beta2 receptors in the heart and the lungs • Best blood pressure lowering result is achieved when given with a diuretic agent – Negative inotropic – Negative chronotropic – Negative dromotropic • Prototype: propranolol (Inderal) • Adverse effect: bronchoconstriction • Hold dose if HR less than 50 Miscellaneous vasodilators p492 • Vasodilators directly dilate the peripheral arterioles • Hydralazine: dilates peripheral arterioles – Side effects: palpitations, tachycardia • Minoxidil: dilates peripheral arterioles – Side effect: growth and thickening of fine body hair – Rogaine is minoxidil in topical dosage form marketed as treatment for male pattern alopecia Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors p492 • Called ACE inhibitors (-pril) • Action: antagonists to the renin angiotensin-aldosterone system • ACE inhibitors prevent: – Angiotensin I conversion to angiotensin II • Prototype: Lisinopril ACE Inhibitors: Side Effects p492 • • • • • • Fatigue Dizziness Headache Mood changes Impaired taste Dry, nonproductive cough – Persistent cough could be indication to withdraw Lisinopril • Loss of ability to ejaculate, erectile dysfunction Angiotensin II Antagonists p492 • Allow angiotensin I to be converted to angiotensin II, but block the receptors that receive angiotensin II – Block vasoconstriction and release of aldosterone • Well-tolerated – Coughing not a concern • Examples – irbesartan – losartan – valsartan Calcium Channel Blockers p493 – Prevent calcium from entering muscle cell thereby reducing muscle contraction • Relax peripheral arterioles and reduce peripheral resistance • Prototype: verapamil (Calan) • Side effects – Hypotension – palpitations – Tachycardia – peripheral edema Hypertensive emergencies p494,500 • Diastolic pressure exceeding 120 mm Hg with evidence of end organ damage. • Agents for treating hypertensive emergencies: diazoxide nitroprusside sodium Sodium restriction in diet p502-503 • Nurses teach label reading • Signs of hyponatremia: • • • • • weakness confusion abdominal cramps muscle twitching If severe, seizures may occur. Limiting adverse effects of antihypertensive meds p505 • Non-compliance with medication schedule has many causes • Do not discontinue the med, but inform health care provider of the side effects so alterations can be made. Patient teaching • • • • • • • • Teach pt to take BP daily and keep log Teach at least one family member to take pt BP Smoking cessation Teach signs and symptoms of sodium or potassium depletion Avoid activities that place stress on cardiovascular system. Avoid straining to pass stool Avoid heavy meals Teach lifestyle modifications