* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download diuretics
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
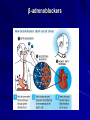
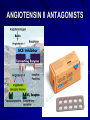
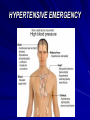
Clinical Pharmacology of Drugs for Controlling Vascular Tone. ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS I. DIURETICS Bumetanide, furosemide, hydrochlorthiazide, spironolactone, triamterene II. -BLOCKERS Atenolol, labetalol, metoprolol, propranolol, timolol III. ACE INHIBITORS Captopril, benazepril, enalapril, fosinopril, lisinopril, moexipril, quinapril, ramipril IV. ANGIOTENSIN II ANTAGONIST Losartan V. Ca++CHANNEL BLOCKERS Amlodipine, diltiazem, felodipine, isradipine, nicardipine, nifedipine, nisoldipine, verapamil VI. -BLOCKERS Doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin VII. OTHER Clonidine, diazoxide, hydralazine, -methyldopa, minoxidil, sodium nitroprusside TREATMENT STRATEGIES Treatment of arterial hypertension Drugs of first row -diuretics (furosemid, dichlothiazide, spironolacton) -inhibitors of ACE (captopril, enalapril, ramipril) -antagonists of angiotesine II receptors (АRА ІІ) (losartan) -β-adrenoblockers (anaprilin, atenolol, thymolol) -α-, β-adrenoblockers (labetolol, carvedilol) -Ca ions antagonists (niphedipine, amlodipine, verapamil) Drugs of second row : -α-adrenoblockers (prasosine, terasosine) -agonists of α2 –adrenoreceptors of central action (clopheline, methyldopa) -sympatholytics (reserpin, octadin) -direct vasodilators (molsidomin, hydralasin) New drugs: -imidasolines (moxonidine, rilmenidine) -serotonin receptors blockers (ketanserin) -monateril (calcium antagonist, α2 -adrenoblocker) Mechanism of action of thiaside diuretics in case of arterial hypertension Dychlothiaside (hypothiaside) Oxodolin (chlortalidon, hygroton) Thiaside diuretics Holding sodium and water Volume of circulating blood Peripheral vascular resistance Decreasing of arterial pressure Cardiac output Hydrochlorothiazide+Losartan Thiazide diuretics. Adverse effects: Loop diuretics The loop diuretics act promptly, even in patients who have poor renal function or who have not responded to thiazides or other diuretics. -blockers. Therapeutic uses β-adrenoblockers ACE-INHIBITORS The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (captopril, enalapril, lisinopril, perindopril) are recommended when the preferred first-line agents (diuretics or blockers) are contraindicated or ineffective. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF IACE ANGIOTENSINOGEN sympathetic tone Renin (kidneys) ANGIOTENSIN (inactive) Decrease angiotensine II production ACE IACE Decrease aldosterone production peripheral vessels tone retention of Na+ and H2O bradicinine Decrease of arterial pressure Therapeutic uses ACE inhibitors adverse effects ANGIOTENSIN II ANTAGONISTS Losartan (Cozaar®), Valsartan (Diovan®), Irbesartan (Avapro®), Candesartan (Atacand®). ANGIOTENSIN II ANTAGONISTS CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS -ADRENERGIC BLOCKING AGENTS Prazosin, doxazosin and terazosin produce a competitive block of 1 adrenoreceptors. They decrease peripheral vascular resistance and lower arterial blood pressure by causing the relaxation of both arterial and venous smooth muscle. These drugs cause only minimal changes in cardiac output, renal blood flow, and glomerular filtration rate. Postural hypotension may occur in some individuals. Prazosin is used to treat mild to moderate hypertension and is prescribed in combination with propranolol or a diuretic for additive effects Prasosine (α 1 – –adrenoblocker adrenoblocker)) CENTRALLY-ACTING ADRENERGIC DRUGS Clonidine – 2-agonist – diminishes central adrenergic outflow. Clonidine does not decrease renal blood flow or glomerular filtration and therefore is useful in the treatment of hypertension complicated by renal disease. Because it causes sodium and water retention, clonidine is usually administered in combination with diuretic. CENTRALLY-ACTING ADRENERGIC DRUGS CENTRALLY-ACTING ADRENERGIC DRUGS -Methyldopa. This 2-agonist is converted to methylnorepinephrine centrally to diminish the adrenergic outflow from the CNS, leading to reduced total peripheral resistance and a decreased blood pressure. Because blood flow to the kidney is not diminished by its use, methyldopa is especially valuable in treating hypertensive patients with renal insufficiency. The most common side effects of -methyldopa are sedation and drowsiness. VASODILATORS VASODILATORS Mechanisms of Action of Vasodilators. Mechanism Examples Release of nitric oxide from drug or endothelium Nitroprusside, hydralazine, nitrates, histamine, acetylcholine Reduction of calcium influx Verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine Hyperpolarization of smooth muscle membrane through opening of potassium channels Minoxidil, diazoxide Activation of dopamine receptors Fenoldopam PRINCIPLES OF THERAPY Therapeutic Regimens Once the diagnosis of hypertension is established, a therapeutic regimen must be designed and implemented. The goal of management for most clients is to achieve and maintain normal blood pressure range (below 140/90 mm Hg). If this goal cannot be achieved, lowering blood pressure to any extent is still considered beneficial in decreasing the incidence of coronary artery disease and stroke. HYPERTENSIVE EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSIVE EMERGENCY (intravenously) Drug Sodium nitroprussid Dose 0,5-10 mcg/kg/min (dropply) Nitroglycerinum 5-10 mcg/kg (dropply) Onset immediately Side effects nausea, vomiting, muscles, sweating 2-5 min tachicardia, vomiting, fibrillation of flushing, headache, Diazoxidum 50-100 mg (quickly) 300 mg (during 10 min) 2-4 min nausea, vomiting,, hypotension, tachicardia, flushing, redness of skin, chest pain Apressinum 10-20 mg 10 min flushing, redness of skin, headache, vomiting Furosemidum 20-60-100 mg during 10-15 sec 2-3 min hypotension, fatigue Clophelinum 0,5-1 ml 0,01 % solution (in 15-20 ml 0,9 % solution NaCI slowly) 15-20 min somnolence Anaprilinum 5 ml 0,1 % solution (in 20 ml 0,9 % NaCI solution slowly) 20-30 min bradicardia Magnesium sulfas 5-10-20 ml 25 % solution (i. v. very slowly or dropply) 15-20 min redness of skin Labetololum 20-80 mg (slowly – 10 min) or 2 mg/kg (dropply); the whole dose – 50-300 mg 5-10 min nausea, dizzeness vomiting,, hypotension,