* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of asthma
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
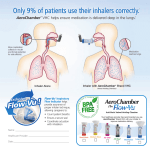
Presented by : Abdulhadi Burzangi . Pharm.d 1 Key Point.. I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Background of Asthma. Clinical presentation. Drug used in asthma. Stepwise approach for managing asthma. Steps for using inhaler. Case. 3 I- Background •Definition : - Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of airway associated with inflammation, obstruction and increase airway hyperresponsiveness. 4 • Types of asthma : Intermittent Persistent Mild Moderate Severe symptoms < 2 days/week > 2 days/week but not daily Daily Through out the day Night time awakening < 2 days/month 3-4 days/month > 1 day/week Often 7 days/w SABA use for symptoms control < 2 days/week > 2 days/week Daily Several time per day Interference with normal activity None Minor limitation Some limitation Extremely limited • Asthma triggers : 1- Allergens. 2- Occupational exposure. 3- Disease. 4- Environmental changes. 5- Emotions. 6- Exercise. 7- Drugs and preservatives. 11- Clinical presentation - In case of chronic ambulatory asthma : 1- Episode of dyspnea. 2- Chest tightness. 3- Coughing ( particularly at night ). 4- Wheezing or a whistling sound when breathing. - In case of severe acute asthma : 1- Severe dyspnea. 2- Chest tightness. 3- S.O.B 4- The patient is able only to say a few words with each breath. 5 111- Drugs used in asthma A. Beta 2 agonist. 1- Short acting beta agonist (SABA). 2- Long acting beta agonist (LABA). B. Corticosteroids (CS). 1- Inhaled. 2- Oral. C. D. E. F. G. Leukotrine receptor antagonist. Mast cell stabilizer. Phosphodiestrease inhibitor. Anti IgE. Anticholinergic. 6 A. Beta 2 agonist • SABA : - e.g : Albuterol . - Uses • LABA : - e.g : 1-Salmetrol - Uses 2-Formetrol . - Side effect of both : 1- Tachycardia. 2- Palpitation. Hypokalemia. 3- Tremor. 47 B. Corticosteroid • Inhaled CS : - e.g : 1- Beclomethasone. • Oral CS : - e.g : 1-predinsone, 2-predinsolone 2- Budesonide. 3- Flunisolide. 4- Fluticasone. 5- Trimcinolone. - Uses 3-methylpredinsolone - Uses 8 • Short term and long term side effect : Short term S.E -Facial flushing. -Appetite stimulant. -GIT irritation. -Mood change. -Acne. -Weight gain. -Hyperglycemia. -Leukocytosis. -Hypocalsemia. Long term S.E -HPA axis suppression. -Growth retardation. -HTN. -Osteoporosis. -Hirsutism. -Myopathy. 9 C. Leukotriene receptor antagonist - e.g : ( Montelukast, Zafirlukast and Zileuton ). - Uses D. Mast cell stabilizer - e.g : ( Cromolyn Na+ and Nedocromil ). - Uses 10 E. Phosphodiestrase inhibitors - e.g : ( Theophylline ). - use - Factors affecting serum theophylline concentration : Decrease Theophylline conc. Increase Theophylline conc. -High protein diet. -Smoking. -Rifampin. -Phenytoin. -Phenobarbital. -Carbamazepine. -High carbohydrate diet. -Systemic viral infection. -Cimetidine. -Erythromycin. -Ciprofloxacin. -Ticlopidine. 11 Other Drugs F. Anti IgE (Omalizumab). G. Anticholinergic (Ipratropium). 13 IV. Stepwise approach for managing asthma. 14 V. Steps for using inhaler. 1. Remove the cap and hold inhaler upright. 2. Shake the inhaler. 3. Tilt your head back slightly and breathe out slowly. 4. Position the inhaler in one of the following ways 5. Press down on the inhaler to release medication as you start to breathe in slowly. 6. Breathe in slowly (3 to 5 seconds). 7. Hold your breath for 10 seconds to allow the medicine to reach deeply into your lungs. 8. Repeat puff as directed. Waiting 1 minute between puffs may permit second puff to penetrate your lungs better. 15 VI. Case K.M is 33years old female , she came to ambulatory care department at last Saturday . She had been bronchial asthma X 13 years . She was complaining of cough, wheezing , chest tightness and drowsiness. The patient said ( sometimes my family want to take me to ED when i had asthmatic attack but i didn’t want to visit ED). She on seretid (Flutacasone/Salmetrol) for her asthma. 16 Subjective : • Chief complaint: - wheezing. - cough. - chest tightness. - drowsiness. • Problem list : - bronchial asthma X 13 years. - iron deficiency anemia. • Social history : • Allergy : - single. - Food > banana … shrimp. - Drugs > no known drug allergy. - Others > dust and costs. 17 Objective : • Vital sings : R.R : 20 rate/min B.P : 130/61 • Weight : 68.6 kg Temp. : 36.8 ْc Pulse : 81 beat/min Height : 150cm. • Past medication : - Inhaled beclomethasone 100 mcg puff bid. - Ventolin (Albuterol). 18 Current medication : - Seretid ( Fluctasone 250mcg + Salmetrol 50mcg )BID. - Ferrose (100 mg iron as iron III hydroxide polymaltose complex). Assessment : - The patient diagnosed with mild persistent asthma. - She doesn’t response to her medication. Plan : - Ventolin solution + Ventolin neublizer. - Ferrose. 19 Recommendation -Check the patient compliance….. -Stop gradually….. -General measure for treating asthma. 20