* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 23. Interventions for Clients with Cardiac Problems
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Infective endocarditis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
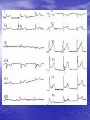
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
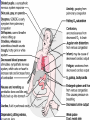
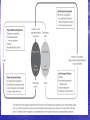
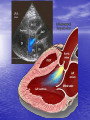
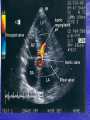
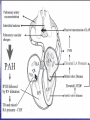
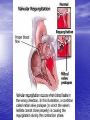
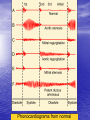
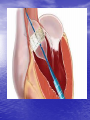
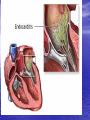
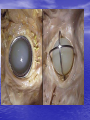
Interventions for Clients with Cardiac Problems Heart Failure • Also called pump failure, general term for the inadequacy of the heart to pump blood throughout the body; causes insufficient perfusion of body tissue with vital nutrients and oxygen • Left-sided heart failure • Right-sided heart failure • High-output failure Etiology • Heart failure is caused by systemic hypertension in 75% of cases. • About one third of clients experiencing myocardial infarction also develop heart failure. • Structural heart changes, such as valvular dysfunction, cause pressure or volume overload on the heart. Left-Sided Heart Failure • Manifestations include: – Weakness – Fatigue – Dizziness – Confusion – Pulmonary congestion – Shortness of breath (Continued) Left-Sided Heart Failure (Continued) – Oliguria – Organ failure, especially renal failure – Death • Assess blood pressure, mental status, breath sounds Right-Sided Heart Failure • Manifestations include: – Distended neck veins, increased abdominal girth – Hepatomegaly (liver engorgement) – Hepatojugular reflux – Ascites – Dependent edema – Weight: the most reliable indicator of fluid gain or loss Assessments • Laboratory • • • • assessment Radiographic assessment Electrocardiography Echocardiography Pulmonary artery catheters Drugs That Enhance Contractility • Digitalis – Digitalis toxicity includes anorexia, fatigue, changes in mental status. – Monitor heart rate and electrolytes. • Other inotropic drugs including dobutamine, milrinone, and levosimendan • Beta-adrenergic blockers Surgical Management • Newer surgical therapies include the following: – Partial left ventriculectomy – Endoventricular circular patch – Acorn cardiac support device – Myosplint Potential for Pulmonary Edema • Interventions include: – Assess for early signs, such as crackles in the lung bases, dyspnea at rest, disorientation, and confusion. – Rapid-acting diuretics are prescribed, such as Lasix or Bumex. – Oxygen is always used. – Strictly monitor fluid intake and output. Valvular Heart Disease • Mitral stenosis • Mitral regurgitation (insufficiency) • Mitral valve prolapse • Aortic stenosis • Aortic regurgitation (insufficiency) Assessment • Client may become suddenly ill or slowly develop symptoms over many years. • Question client about attacks of rheumatic fever, infective endocarditis, and possibility of IV drug abuse. • Obtain chest x-ray, echocardiogram, and exercise tolerance test. Nonsurgical Management • Drug therapy, including diuretics, beta blockers, digoxin, oxygen, and sometimes nitrates • Prophylactic antibiotic • Management of atrial fibrillation, cardioversion • Anticoagulant • Rest with limited activity Surgical Management • Reparative procedures • Balloon valvuloplasty • Direct, or open, commissurotomy • Mitral valve annuloplasty • Replacement procedures Infective Endocarditis • Microbial infection involving the endocardium • Occurs primarily with IV drug abuse, valvular replacements, systemic infections, or structural cardiac defects • Possible ports of entry: mouth, skin rash, lesion, abscess, infections, surgery, or invasive procedures including IV line placement Manifestations • Murmur • Heart failure • Arterial embolization • Splenic infarction • Neurologic changes • Petechiae (pinpoint red spots) • Splinter hemorrhages Interventions • Antimicrobials • Rest, balanced with activity • Supportive therapy for heart failure • Anticoagulants • Surgical management Pericarditis • Inflammation or alteration of the pericardium, the membranous sac that encloses the heart • Dressler’s syndrome • Postpericardiotomy syndrome • Chronic constrictive pericarditis Assessment • Substernal precordial pain radiating to left side of the neck, shoulder, or back • Grating, oppressive pain, aggravated by breathing, coughing, swallowing • Pain worsened by the supine position; relieved when the client sits up and leans forward • Pericardial friction rub Interventions • Hospitalization for diagnostic evaluation, • • • • • • • observation for complications, and symptom relief Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Corticosteroid therapy Comfortable position, usually sitting Pericardial drainage Chronic pericarditis: radiation or chemotherapy Uremic pericarditis: dialysis Pericardiectomy Emergency Care of Cardiac Tamponade • Cardiac tamponade—an extreme emergency • Increased fluid volume • Hemodynamic monitoring • Pericardiocentesis • Pericardial window • Pericardiectomy Interventions • Nonsurgical management • Surgical management – Cardiomyoplasty – Heart transplantation