* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hinduism - Mr
Classical Hindu law in practice wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-Hindu law wikipedia , lookup
2013 Bangladesh anti-Hindu violence wikipedia , lookup
Pratyabhijna wikipedia , lookup
Akhil Bharatiya Hindu Mahasabha wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu nationalism wikipedia , lookup
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Malaysia wikipedia , lookup
Vishishtadvaita wikipedia , lookup
Vishnu sahasranama wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Tamil mythology wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
LGBT themes in Hindu mythology wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
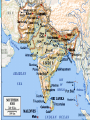
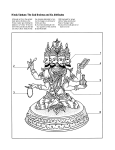
Basic Beliefs Hinduism World’s Oldest Religion Origins can’t be traced No human founder Some believe it existed in 10,000 B.C. 3rd Largest World Religion What is Hinduism? No “one Hinduism” Way of Life Dharma Law that governs all action Ethics and Duties Cycle of Life Samsara beginning less and endless cosmic evolutionary process (universal and worldly) Rebirth Karma Law of cause and effect Part of the Samsaric process Cycle of Life Transmigration & Reincarnation of the soul (Jiva) Soul transmigrates from life to life until it relieves itself from Karmic burden Moksha Spiritual Knowledge of True Self (Atman) and God Liberation from cycle of rebirth (union with Brahman) Everyone will achieve Moksha Hindu Scriptures Shastras – collection of spiritual laws Two types Shruti (heard) “cosmic sound of truth” Smriti (memorized) Scriptures divided into Vedas (common name) Hindu Deities Polytheistic Thousands of gods and goddesses representing different aspects of Brahman Brahman – One Supreme Trinity of Brahma (creator), Vishnu (preserver) and Shiva (destroyer) Hindu Gods Brahma The Creator Hindu Gods Vishnu The Preserver Hindu Gods Shiva The Destroyer Hindu Gods Brahma Vishnu Shiva Ahimsa – practice of non-violence Belief that all life is sacred and should be loved and revered Many are Vegetarians Responsible for the creation of such original concepts and practices as Yoga, Ayurveda, Vastu, Jyotish, Yajna, Puja, Tantra, Vedanta, Karma, etc Holi – Celebrates beginning of Spring Sources http://hinduism.about.com/od/basics/p/hinduismbas ics.htm