* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pediatric Anesthesia A Brief Review of Major Topics
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Infective endocarditis wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
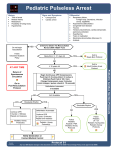
Pediatric Anesthesia A Brief Review of Common Disorders By: Christine Mazza, T4 Diseases with Difficult Airways • Pierre Robin – micrognathia, glossoptosis, cleft palate – Nasal airway, tongue suture, LMA – Pre-op cardiac eval required • Treacher-Collins – facial and pharyngeal hypoplasia, aplastic zygomatic arches, micrognathia, choanal atresia – Narrowing of airway above larynx, LMA useful – Pre-op cardiac eval required • Hurler’s – short thick neck, course facies, macroglossia, large tonsils and adenoids – Post-op subglottic edema common – Cardiac eval pre-op Diseases with Difficult Airways • Goldenhar Syndrome – unilateral (usually) disruption in formation of craniofacial structures and vertebral abnormalities – Difficult airway – Pre-op eval of heart and c-spine • TE fistula – part of VATER syndrome – Awake intubation preferred – Insert tube deeply and pull back until fistula is occluded but both lungs are ventilated • CDH – dyspnea, cyanosis, scaphoid abdomen, BS in chest – Use minimal pressure ventilation to avoid pneumothorax; if sudden cyanosis, assume pneumothorax Review in Pictures Cardiac Abnormalities • Cyanotic Defects (R L) – defect between arterial and venous circulation with outflow obstruction on venous side – Tetralogy of Fallot, truncus arteriosis, transposition of the great vessels – Pre-op treatment of dz, endocarditis prophylaxis, remove air bubbles from IV tubing – OXYGEN! Hydration, gentle ventilation • Acyanotic Defects (L R) – single defect between arterial and venous circulation so that blood flows from high to low pressure – ASD, VSD, PDA, cushion defects – Pre-op treatment of dz, endocarditis prophylaxis, remove air bubbles from IV tubing – PPV, low FiO2 as tolerated • PPHN – persistence or return of fetal circulation after birth – Basically same treatment as Cyanotic defects above – Increase pulm blood flow, hyperventilate Genetic/Hematological Diseases • Hemophilia A – most common inherited coagulation disorder – Oral medications, general anesthesia – Intubation acceptable, but be wary of hemorrhage • Sickle Cell – Pre-op: HYDRATION, transfuse to increase Hct to 30 – Intra-op: HYDRATION, oxygenation, replace blood loss when necessary • Porphyria – demyelination, flaccid paralysis, weakness, autonomic dysfunction – NO barbituates, steroids, etomidate, enflurane, ketamine – Ok to use opiates, local, N2O, isoflurane, helothane, atropine – Exaggerated response to muscle relaxants • Trisomy 21 – microcephaly, macroglossia, CHD, duodenal atresia, atlanto-axial instability, congenital subglottic stenosis – Difficult airway –consider ETT 1 size down – Decreased MAC, exaggerated response to muscle relaxants – Pre-op cardiac work up, c-spine films? Resources • Bell, C.; Kain, Z. The Pediatric Anesthesia Handbook Mosby-Year Book, Inc, St. Louis: 1997. • Infosino, Andrew. “Pediatric Upper Airways and Congenital Anomalies”. Anesthesiology Clinicals of North America. 20 (2002): 747-766. • Macksey, Lynn Fitzgerald. Pediatric Anesthetic and Emergency Drug Guide. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Ontario Canada: 2009. • Stoelting, R; Dierdorf, S. Handbook for Anesthesia and Co-Existing Disease. Churchill Livingstone Publishing, Philadelphia: 2002. • http://www.theaba.org/Home/anesthesiology_initial_certification