* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Basic Pharmacology and Selected Therapies
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
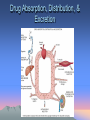
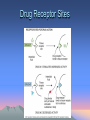
Introduction to Basic Pharmacology and Selected Therapies Chapter 16 Pgs 218-230 Overview • • • • • Basic principles of drugs Administration and distribution of drugs Drugs and receptors Prescription and medication orders Other common traditional forms of therapy – – – – • Physiotherapy Occupational therapy Speech/language pathologist Nutritionist/dietitian Complementary or alternative therapies – – – – – Osteopathy Chiropractic Homeopathy Aromatherapy Asian concepts of disease and healing • acupuncture Basic Principles • Pharmacology • Sources of drugs – Natural – Synthesized Drug • Substances that alters biologic activity • Prescribed for many reasons: – – – – – – – – To promote healing To cure disease To control or slow progress of disease To prevent disease To decrease risk of complications To increase comfort level As replacement therapy To decrease excessive activity in body Drug Effects • Exerts therapeutic action by stimulating or inhibiting cell function • Block effects of biochemicals in tissue • Have physical/mechanical action • Classified by primary pharmacologic action and effect • Indications vs. contraindications • Side effects vs. adverse effects Specific Forms of Adverse Effects • • • • • Hypersensitivity Idiosyncratic reactions Iatrogenic reactions Teratogenic Interactions – Synergism – Antagonism – Potentiation Administration and Distribution of Drugs • 1st consideration is dosage – Amt required to produce specific desired effect in an adult – “loading dose” – Should not increase prescribed dose (Duh!) • Freq important in maintaining approp blood levels – Dosing schedule based on: • Absorption • Transport in blood • ½ life of drug Factors affecting blood levels Factors Affecting Blood Levels of Drug • Also dependent on individual’s: – Circulation – Age – Weight – Ability to metabolize and excrete drug • What organs have that responsibility? – Genetic factors – State of health/illness Administration and Distribution of Drugs • Drug enters body blood target site exerts effect metabolized & secreted • Routes for administration – Orally – Parenterally – Inhalation – Topical – Rectal Drug Circulation • Often bound to plasma proteins • Some of drug may follow different pathway • Enters target tissue/organ ISF exerts effect • Blood brain barrier Drug Absorption, Distribution, & Excretion Drugs and Receptors • Many in body • Respond to natural substances – – – – Enzymes Hormones NT Electrolyte • Many meds at receptor sites in cells or on cell membrane – Stimulate receptor (agonist) – Block receptor (antagonist) Drug Receptor Sites Prescription and Medication Orders • Prescription is a legal signed document – Must include: • • • • Pt’s name, address, age Prescriber’s name, address, identification Date Name of drug, amount, dosage, route, directions, # refills • Has chemical name, generic name, trademark name • FDA regulates • OTC • Official schedules Clinical Research • Preliminary studies • Trials • Research – Experimental group – Control group (placebo) Physiotherapist • Assess physical function and words to restore any deficit and prevent further dysfunction • Pts with acute neurologic, musculoskeletal, cardiopulmonary disorders • Rehabilitation and long-term care Occupational Therapy • Provide a functional assessment of pt. capabilities related to normal activities of daily living (ADL) • Goal is to assist in max. func. & indep. Speech/Language Pathologist • Specialist in assessment and treatment of those with communication and swallowing problems • Infants elderly Nutritionist/Dietitian • Advise to individuals and groups – On nutritional demands – Food management best suited to diagnosis • Consulted regarding extreme diets, anorexia Alternative Therapies • Considered to be on outside range of traditional Western medication • Many have roots in Asia – Emphasis on preserving healthy lifestyle – Holistic approach • Increase in usage • Varying degrees of training, professional regulation Osteopathy • Medical Drs. • Use traditional treatments and procedures – Also promote body’s natural healing processes Chiropractic • I love them!!!! • Based on concept that one’s health status depends on state of N.S. Homeopathy • Goal is to stimulate the immune system and natural healing power in the body Aromatherapy • • • • • • Essential oils extracted from plants Rubbed on skin, inhaled Chamomile calming, sleep-inducing Lavender soothe headache, calming Eucalyptus stress reliever Rosemary relieves muscle and joint pain Asian Concepts of Disease & Healing • Based on balance (or imbalance) of life energy – Called qi • Disease caused by excess/deficit of qi • Qi derived from three sources – Inherited or ancestral factors – Food ingested – Air breathed in Asian Concepts • Imbalance between yin and yang – Caused by changes in • • • • • Diet Stress Metabolism Activity Environment Asian Concepts • Meridians – Specific channels in body • Qi flows along them • May be located far from organ from which it is named • All bilateral except: – Midline anterior (conception vessel) – Midline posterior (governor’s vessel) Asian Concepts • Acupoints – To access qi and it’s flow – Each has specific action or property • Moving qi or blood, decrease pain, heating, cooling, drying, calming, emotions • Disharmony may involve many acupoints and meridians Acupuncture • Chinese therapy (3000 years old) • Involves inserting very fine needles into merdian acupoints – Classically 365 acupoints • Only 150 used today • Each point has specific therapeutic action • Treatment – 5-15 needles – Connected to low-level electrical current – Period of 30-45 min