* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anaesthetic Drugs
Survey
Document related concepts
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Epidural administration wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
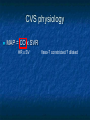
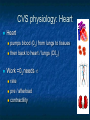
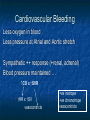
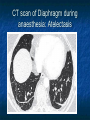
Anaesthesia 13.30 - 14.30 Dr Rob Stephens Physiological and Pharmacological principles 14.30 - 15.30 Dr Andy Badacsonyi Anaesthesia in the 21st century 15.30 - 15.45 BREAK 15.45 - 16.45 Dr Brigitta Brandner Acute Pain Management Physiology and … Dr Rob Stephens Thanks to Drs James Holding and Maryam Jadidi Contents Introduction Physiology CVS, RS, NS, Other Pharmacolgy Anaesthetic/ Hypnotic Agents Neuromuscular Paralysis & Reversal Analgesia Others, CVS, Gasses, Fluids Introduction General word: website, documents, coming to theatre Introduction Anaesthesia is more than Physiology and Pharmacology! Surgery vs Anaesthesia Outside theatre CVS physiology O2 + C6H12O6 CO2 + H2O ATP O2 delivery =Amount of O2 to tissues per minute =Cardiac Output x O2 content of blood x HR x SV Hb x Sa02 x constant CVS physiology MAP = CO x SVR HR x SV Vaso-? constricted ? dilated AT REST 5 l/min RIGHT HEART L H 100% CVS physiology: Heart Heart 4-5% pumps blood (02) from lungs to tissues then back to heart / lungs (C013-15% 2) Work =02 needs rate pre / afterload contractility Heart 7% Brain 9% Gastrointestinal 20-25% Kidneys 20% 15-20% Muscles Anaesthesia and CVS CVS effects.. Anxiety, illness, walking to theatre, pain Induction of general anaesthesia or onset of epidural/ spinal anaesthesia Cardiovascular - active drugs Intubation Surgical stimulation / trauma Haemorrhage Extubation ?Recovery or complication Cardiovascular changes ‘artists impression’ version often filled in! Preopera tive Induction of anaesthesia Incision Surgical stimulation Cardiovascular Bleeding Less oxygen in blood Less pressure at Atrial and Aortic stretch Sympathetic ++ response (+renal, adrenal) Blood pressure maintained … ↑ CO x ↑ SVR ↑HR x ↑SV vasocontricts +ve inotrope +ve chronotrope vasocontricts Respiratory Upper – Airway Lower- Trachea, lungs, muscles Respiratory- Airway Anaesthesia ‘Obtunds’ airway =“Airway obstruction’ = no airflow = no 02 = Badness Respiratory- Airway Keep Airway open: Airway manoeuvres (chin lift etc) Airway devices- above vs blow cords Above Vocal Cords eg , gudel, LMA Below Vocal Cords - Into trachea = intubation, paralysis Guedel / Oro-Pharyngeal size 4 size 3 Adult male Adult female Guedel Laryngeal Mask Airway Respiratory- Airway Respiratory- Lower/ Lungs Spontaneous vs Ventilated Lungs smaller depth Drugs respiratory rate Small airways / Alveolar collapse Can’t cough – secretions = ‘pulmonary shunt (vs deadspace) Hypoxaemia, persists postoperatively CT scan of Diaphragm during awake spontaneous breathing CT scan of Diaphragm during anaesthesia: Atelectasis Gastrointestinal General Anaesthesia relaxes gastro-oesophageal sphincter Fluid up oesophagus ?into lungs starvation postoperative vomiting Other drugs (eg analgesia) Neurology Many Effects GA drug induced reversable unconsciousness Many reflexes (airway, gag, CN) Awareness +/- NMJ paralysis Physiology 2(3) factors determining blood pressure How does GA affect these? 3 words about GA on resp system Contents Introduction – the classical triad Introduction – general principles Hypnotic Agents Neuromuscular Paralysis + Reversal Analgesia Cardiovascular Drugs – up and down Fluids and Gasses are drugs too! Pharmacology Introduction Anaesthesia ‘classical triad’ Hypnotic agent- unconsciousness Gas or IV Analgesia Neuromuscular Paralysis Induction, Maintenance, Emergence, Recovery Basics of anaesthesia: diagrams, handout & lecture Introduction - Principles Pharmacokinetics What the body does to the drug Absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination Pharmacodynamics What the drug does to the body – ie it’s effects CVS, RS, GI, NS, Other , Side effects Typical Anaesthesia Intravenous induction Propofol Short acting opiate - e.g. fentanyl Hypnotic ‘anaesthetic’ - e.g. propofol Set up of anaesthetic maintenance - e.g. sevoflurane vapour in oxygen and air Specific muscle paralysis may be needed Definitive analgesia Anti-emetic Others Hypnosis: Propofol Hypnosis: Propofol (and others) IV Redistributed out of CNS metabolised CVS - CO x SVR = MAP RS airway and lungs NS pain on injection Maintenance: Volatiles Oxygen Air Sevoflurane Maintenance Sevoflurane (‘SEVO’) Used for gaseous induction. Desflurane Isoflurane CO x SVR = MAP Gases, inhaled, little metabolised, exhaled CVS: CO x SVR = MAP RS- irritant, bronchodilate NS Given with Oxygen /Air /Nitrous Oxide MAC = minimum alveolar concentration Muscle Paralysis Neuromuscular blockers Depolarising Suxamethonium Non-depolarising Atracurium Vecuronium Rocuronium Neuromuscular blockers Depolarising Suxamethonium 2x Ach molecules Activates receptor Non-depolarising – competitive vs ACh Atracurium Vecuronium Rocuronium Nicotinic ACh Receptor Reversal of Paralysis Neostigmine Blocks cholinesterase Stimulates nicotinic and muscarinic Given with an anticholinergic Sugammadex Analgesia – Dr B Systemic Simple- paracetamol 1g NSAID – Diclofenac etc Opioids eg morphine 2mg bolus Others – Ketamine Regional – spinal / epidural / blocks Local - infiltration Uppers Anticholinergics Atropine Glycopyrulate 200-600μg Symatheto-mimetics 1 agonists Phenylepherine Metaraminol 0.25-0.5 mg Ephedrine mixed and adreno agonist MAP = 1 1 2 CO x SVR Downers More anaesthetic or opiate / analgesia Short acting -blockers (labetalol, esmolol) Short acting blockers GTN MAP = CO x SVR Clonidine - 2 agonist clonidine Antiemetics Antiemetics General- Hydrate, anxiety, gastric decompress Cyclizine anti-histamine Ondansatron 5-HT3 receptor antagonists S/E – constipation + long QT Prochlorperazine (‘Stematil’) – DA and mACh receptor antagonist S/E – tachycardia and other anti-cholinergic effects S/E – extrapyramidal Dexamethasone glucocorticoid S/E – deranged glucose control Fluids and Gasses are drugs too! Oxygen is a ‘drug’ Intravenous fluids Colloids Crystalloids Blood and products Articles on website / youtube General Advice Can always give more – can’t take away Caution in Unwell Elderly Hypovolaemic Lots of ways to anaesthetise- don’t worry