* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Impact of the Crusades
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Livonian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Savoyard crusade wikipedia , lookup
House of Lusignan wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Arsuf wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of the Crusader states wikipedia , lookup
First Crusade wikipedia , lookup
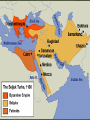
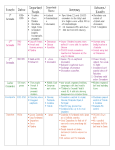
Nunc Agenda: Based on your homework from last night and your knowledge of the Crusades, think of an answer for the Quaestio During their overland journey to the Holy Land, Crusader armies, led by nobles, stopped in Constantinople, met Emperor Alexius, and promised him the land they conquered After a 9-month siege, Crusaders conquered Antioch, slaughtered Muslim inhabitants, and pillaged the city They did not return the land to Alexius They continued south conquering cities including Jerusalem, which Muslims and Jews fought together to defend Four “Crusader States” were established: The County of Edessa The Principality of Antioch The County of Tripoli The Kingdom of Jerusalem Landless Nobles now had lands of their own After almost fifty years of relative peace, Muslims reconquered Edessa, sparking a new Crusade The King of France and the King of Germany each led armies to attack Damascus in Syria, but they were defeated, AND Damascus joined with the Seljuks against the Crusaders (Crusade Fail!) Muslim weakness lack of unity Seljuks controlled Syria, Fatimids controlled Egypt 1147- Saladin (Salahuddin) became leader of both Egypt and Syria, reconquered Jerusalem and other Crusader lands for the Muslims In response, Pope called for Third Crusade HRE Frederick I Barbarossa, French King Philip II of France, and King Richard the Lionheart of England led armies to take back Jerusalem, but they were unsuccessful Saladin agreed to allow Christian pilgrims into Jerusalem Pope Innocent III called for a Fourth Crusade Lacking the funds to go all the way to Jerusalem, the Crusaders instead sacked Christian Constantinople and established a Latin Empire in Byzantine land There were other smaller Crusades in the following years but they had little impact Directions: Each desk is a station with a number 1-6. Read the selection and then answer the associated question on your sheet. After 4 minutes, you will switch the next station, and this will continue until all 6 are done. As you work, consider the quaestio, and add to its answer as you complete the stations.