* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Business Cycles
Workers' self-management wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Circular economy wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
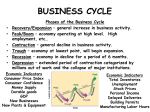
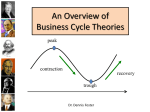
Business Cycles Economic Performance Business Cycles • Fluctuations or changes in a market system’s economic activity • Changes are measured by increases or decreases in real GDP • Duration of upturns or downturns can last from a few months to several years Phases of the Business Cycle • • • • Expansion-recovery Peak-prosperity Contraction-recession Trough-depression Expansion – Recovery • People, optimistic about the future, begin to buy again, even “big ticket” items • Housing starts go up; productivity increases in the manufacturing sector. • Stores order more inventory; factories gear up and hire more people. • More money gets into circulation. • Borrowing increases, both in the buyer and producer sectors. Peak - Prosperity • Economy begins to reach the limits of its resources. • Demand begins to exceed supply, resulting in rising wages, prices, and interest rates • When all this happens, people think twice about “big ticket” credit items • Consumers gradually cut back on spending. • Producers think twice about opening new plants and hiring new workers with wages so high. Contraction - Recession • • • • People stop spending; Inventories build up in stores; Stores order fewer goods; Factories cut back on production, hire workers at lower wages. • People begin to lose optimism and buy even less. • GDP declines. • When it has declined for two quarters (half a year), we classify that we are in a recession. Trough - Depression • If the recession hangs on, producers lay off workers. • Both producers and sellers find themselves stuck with inventories. • People hold off borrowing, so demand for loans is down and loan rates decline. • There sits everyone at the bottom of the trough until some kick in the pants causes people to get optimistic again and start buying more goods and services. External Causes affecting the Business Cycle • These are causes not part of the economic system itself. Examples are: – Instability in other parts of the world can affect the economy (such as war, OPEC embargo) – Technological breakthroughs that allow us to produce more with the same resources can stimulate the cycle’s expansion phase and put off contraction. – Social and political changes can affect the economy. The election of FDR in 1932 had a short expansive effect on the economy. Watergate’s aftermath had the opposite effect in 1973-1975 Internal Causes Affecting the Business Cycle • These are causes which are part of the economic system itself. Examples are: – Capital. If equipment all wears out at about the same time, or if it goes out of date, it has to be replaced. All those new orders spur the economy into an expansion phase. – Inventories. It’s holiday time, so stores are ordering large inventories. Factories are humming. If the holiday season doesn’t go well, stores will hold off ordering, production will go down, layoffs will occur, etc.. – Aggregate Demand. If everyone decides to hide his money in his mattress, spending goes down and the economy contracts. If people decide to save less, production goes up. – Government activity. If the government increases the money supply, it can encourage expansion. If it increase the supply too rapidly, there may be “too many $$ chasing after too few goods” and inflation can occur. If the government scraps the NASA space program, all sorts of producers could be left “home alone”. Business Cycle For each of the following headlines, which phase of the business cycle is the U.S. in? • Durable goods orders slip 8%; factory orders are piling up. • Recession - contraction • Housing industry booms as new housing starts are up 15%. • Recovery - expansion • Ford Motor Company announces 15-week delay in delivery of new models to dealership due to successful selling season. • Prosperity - peak • Unemployment drops 1% for the fourth straight month. • Recession - contraction • Bureau of Statistics reports new business failures are at an all time high. • Depression - trough • Installment debt rises as consumers go on spending spree. • Recovery - expansion • Obama Administration fears tight credit policy of FED will slow economic expansion. • Recession - contraction