* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download business cycles - Ms. Soris` Website
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
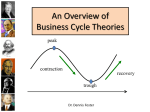
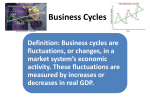
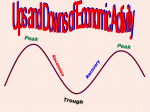
BUSINESS CYCLES PHASES AND INFLUENCES ON THE BUSINESS CYCLE CHAPTER 10, SECTION 2 BUSINESS CYCLES Business cycles are fluctuations, or changes, in a market system’s economic activity. These fluctuations are measured by increases or decreases in real GDP. PHASES OF THE BUSINESS CYCLE Expansion and Recovery Peak Contraction or Recession Trough EXPANSION A period of economic expansion and growth PEAK A high point at which the economy is at it’s strongest and most prosperous. At a peak, high consumer demand encourages producers to use plant capacity and more fully to hire workers. CONTRACTION When real GDP stops increasing, the business cycle enters a period of business slowdown known as a contraction or a recession. A recession is a decline in real GDP for two or more consecutive quarters (6 months or more) DEPRESSION Prolonged and severe recessions such as the Great Depression of the 1930’s The Great Depression was the most severe contraction in US economic history. TROUGH The final stage in the business cycle Occurs when demand, production, and employment reach their lowest levels. Following the trough, the economy enters a period of recovery and the expansion phase begins once again.