* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 30: Business Fluctuations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
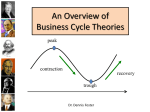
Chapter 30: Business Fluctuations Introduction - Business Cycles are alternating periods of ups and downs in the economy. Phases of the Cycle - A business cycle shows four distinct phases: Peak Recession Tough Expansion Trough - A Trough is the lowest point in a business cycle. - A Depression is a severe trough. Expansion - During a Expansion phase, output expands and income increases. Peak - In a Peak phase, real GDP is at its highest level. Recession - During the Recession phase, income and consumption decline. Length and Intensity of Phases - Business cycles vary in frequency and intensity. Economic Causes of Business Fluctuations The Under-Consumption Theory - Variations in consumer spending cause economic fluctuations. The Volatile Investment Theory - Changes in inventory investment cause fluctuations in economic activity. - Inventory Cycles are the cycles of low inventory and production during recession, and high inventory and production during good economic activity. The Expectations Theory - Changes in expectations cause business cycles. The Innovations Theory - Innovations are a prime cause of business cycles. The Monetary Theory - Changes in the availability of money and interest rates cause business fluctuations. The Multiplier-Accelerator Theory - The Principal of Acceleration suggests that the level of investment is proportional to the rate of change of output. - The capital-output ratio is the ratio of the value of capital to total output. (eg. Its takes $4 worth of capital to produce $1 of output per year) - A change in income leads to an accelerated change in investment. - Required Investment = v(Change in Total Output) K = required capital stock Y = Total Output K/Y = v - Multiplier-accelerator interaction intensifies the business cycle. Politics and the Business Cycle - The Political business Cycle is caused by the government’s use of its spending and taxing powers to secure its political future. The Real Business Cycle - The Real Business Cycle theory suggest that the main causes of business cycles are shifts in aggregate supply. Have we Conquered the Business Cycle - Through the correct use of stabilization policies, we have managed to avoid severe depressions. Forecasting Business Cycles - Leading Indicators turn downward before the cycle peaks and upward before the trough. - Coincidental Indicators coincide exactly with the business cycle. - Lagging Indicators turn downward after the cycle peaks and upward after the trough. - Economists use leading indicators to help them forecast business cycles.