* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Business Cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
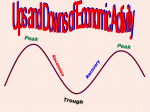
The Business Cycle The Business Cycle may have 4 or 5 phases. Phases of the Business Cycle • • • • • Peak Contraction* (Recession and Depression) Trough Recovery** Expansion Phases of the Business Cycle in Detail • Peak – when real GDP stops rising, the height of economic expansion • The economy is at full employment • Real output is close to capacity • The price level is likely to rise during this phase Phases of the Business Cycle in Detail • Contraction - a period of economic decline marked by a fall in real GDP. • Falling output generally causes unemployment to rise • Inflation is falling Phases of the Business Cycle in Detail • Trough – The lowest point of economic decline, when real GDP stops falling. • This phase of the cycle may be short-lived or long Phases of the Business Cycle in Detail • Recovery- The recovery is the period when Real GDP is rising; it begins at the trough and ends at the initial peak. Phases of the Business Cycle in Detail • Expansion -a steady, long term rise in real GDP. Economic Growth. • • • • • Stock Market is Strong Increase Confidence Inflation Remains Low Falling Unemployment Business Prosperity Business Cycle Issues • Recession (Contraction) – a prolonged economic contraction, of at least 6 months (2 consecutive quarters). • Usually lasting 6 to 18 months. • Typically marked by rising unemployment between 6 to 10 percent. Business Cycle • An entire business cycle is measured from Peak to Peak. • The typical Business Cycle is approximately four to five years. • Although some have been shorter and longer. Business Cycle Issues • Depression – an especially long or prolonged recession. • High Unemployment and low output.