* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download here
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
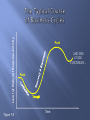
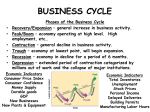
Sec. 2 (Read all of Sec. 2) A modern industrial economy repeatedly goes thru good times, then bad, then good…. it goes thru cycles Why is it important to understand the nature of business cycles? The business cycle directly impacts our daily lives We are continually faced with decisions that can enable us to take advantage of “good” times… and lessen the hurt of the “bad” times Phase 1: Expansion period of prosperity Typical characteristics: MANY NEW BUSINESSES OPEN STRONG EMPLOYMENT FACTORIES WORKING AT OR NEAR FULL CAPACITY CONSUMER SPENDING IS STRONG Expansion has ceased… businesses may have begun to cut back or postpone new spending Job creation slows Phase 3 From a peak ( where GDP levels off) GDP begins to decline… contraction occurs: BUSINESS ACTIVITY SLOWS noticeably UNEMPLOYMENT RISES FACTORIES WORK AT LESS THAN FULL CAPACITY CONSUMER SPENDING WEAKENS If a contraction lasts at least 2 quarters (6 months), we are said to be in a “recession” A prolonged recession or one that is particularly severe is called a “depression” factories cut back production and lay off workers in large #s Consumers cut back on purchases More consumers & biz are late on loan payments…increasing loan defaults occur Fewer new businesses open, many established ones fail Home foreclosures may rise The lowest point is called the trough (“troff”) biz cycle enters the recovery and expansion phase (GDP grows)… Employment rises…new businesses open…spending increases eventually growth slows…then stalls…contraction begins And the cycle continues… Level of National Business Activity Figure 7-8 Peak AND THE CYCLE CONTINUES… Peak Time 4 Main Variables Impact the business cycle When the economy is expanding, firms expect sales & profits to keep rising. Therefore, they are more willing and likely to invest in new equipment , expansion, etc. investment tends to create jobs and increase output, helping to perpetuate the economic expansion low interest rates = encourages borrowing & buying on credit (individuals & firms) Demand for goods/svcs. grows Important: Stronger demand for goods/services motivates firms to hire more people to increase output Int. rates today: high or low? Optimism/confidence = strong consumer spending (opposite is true, too… weakening confidence means weakening spending by consumers) Repercussions from an outside event (a war, natural disaster, etc.) EG: 9/11/2001 Of all the factors that affect the biz cycle, this is most difficult to predict Could be a positive shock (eg, discovery of huge oil deposit) Economists collect data on a regular basis to measure current conditions as well as to forecast future trends. Economic Indicators: 3 Categories A. “Leading indicators” Changes to these data change suggests what will happen to the cycle in the near future (yellow traffic light) Some Examples: 1. # of building permits issued 2. # of new claims for unemployment insurance 3. survey of inventory levels B. Coincident Indicators Changes to these data occur at approx. the same time as the conditions they signify. In our traffic light example, the pedestrian walk signal would coincide (happen) at about the same time as a green. Example: 1. Personal Income C. Lagging Indicators change after the economy as a whole does Examples: Avg. length of unemployment Great Depression (1929-1940) 1946 Recession (returning GIs) 1973 Recession (external shock) 1990s Expansion (dot.com bubble) 2007 Recession (housing collapse) 2000 Peak 9/11 Gr. Dep. begins Post WWII Recession 1990s Boom begins 2007 Gr. Recession Begins