* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 26-3: Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
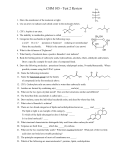
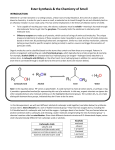
26-3: Carboxylic Acids and Esters Carboxylic Acids (Organic Acids) • Functional group: carboxyl (combines carbonyl and hydroxyl) _______ • General formula: _____ or R-COOH Naming Carboxylic Acids • IUPAC 1. Name longest hydrocarbon chain, add “-oic acid” to root word. 2. Name any branches as necessary. Properties of Carboxylic Acids • Long chain carboxylic acids are known as fatty acids. • Very polar; soluble in water. • Undergo hydrogen bonding, therefore higher boiling points. Esters • Functional group: __________ • General formula: ____ (R-COOR) • Formed from rxn of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. Naming Esters • Based on the alcohol and carboxylic acid it formed from. • Change the name of the alcohol to end in –yl. • Take the name of the acid and add “–oate” to it (if IUPAC) or “-ate” (if common. Ester examples • Ester formed by reacting ethanol and propanoic acid. – Ethyl propanoate • Ester formed by reacting formic acid and propanol. – Propyl formate Properties of Esters • Polar, but do not form hydrogen bonds. Therefore, boiling points are lower than alcohols or acids. • Have very distinctive fragrances (ex: orange, banana, apple, wintergreen, rum, pineapple)