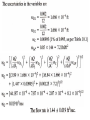* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture Presentation Chp-10
Drag (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Wind-turbine aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Stokes wave wikipedia , lookup
Magnetorotational instability wikipedia , lookup
Lattice Boltzmann methods wikipedia , lookup
Coandă effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Airy wave theory wikipedia , lookup
Compressible flow wikipedia , lookup
Hydraulic machinery wikipedia , lookup
Flow measurement wikipedia , lookup
Flow conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fluid thread breakup wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli's principle wikipedia , lookup
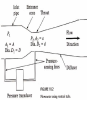
CHAPTER 1O <The Last Chapter> Measuring Fluid Flow Rate, Fluid Velocity, • Bernoulli equation takes the form of where V is the fluid velocity, P is the fluid pressure, z is the elevation of the location in the pipe relative to a specified reference elevation (datum), ρ is the fluid density, and g is gravity The velocities at two axial locations in the duct with different areas are related through the conservation of mass equation, where, A is the duct crosssectional area and is the fluid mass flow rate (e.g., kg/s). For an incompressible fluid, the density is constant. is usually written in the form: Equations can be combined to obtain an expression The theoretical basis for a class of flow meters in which the flow rate is determined from the pressure change caused by variation in the area of a conduit. is used to account for nonideal effects. and a parameter called the Reynolds number, which is defined as When z1 = z2 Flow Rate Equation becomes as follows: The Reynolds number is a dimensionless parameter, The venturi , thus operating within the range of data in Table 10.1. Coriolis Mass Flowmeter The Coriolis force is a force that occurs when dynamic problems are analyzed within a rotating reference frame. Useful flowmeters based on this effect are now widely used in the process industries. Consider a fluid flowing through the U-shaped tube shown in Figure 10.13(a).The tube is cantilevered out from a rigidly supported base. An electromechanical driver is used to vibrate the free end of the tube at its natural frequency in the y direction. The amplitude of this vibration will be largest at the end of the cantilever and zero at the base. Consider an instant in time when the tube is moving in the -y direction. The fluid moving through the tube away from the base will not only have a component of velocity in the x direction but also in the -y direction, and the magnitude of this y component will increase with distance from the base. As a fluid particle moves along the tube, it is thus accelerating in the -y direction. This acceleration is caused by a Coriolis force in the -y direction applied by the tube wall. The resultant reaction on the tube wall is a force, F in the *y direction. For the fluid returning to the base, the y component of fluid velocity is decreasing in the flow direction. This results in a Coriolis force on the tube wall in the -y direction.