Effect of Downstream Flapping Plate on the Flow Field
... The effective control of the vortex shedding behind the cylinders becomes an important issue due to their wide range of practical applications like flow past heat exchangers, buildings, suspension bridges, road vehicles to name a few. The vortex shedding the bluff bodies can sometimes be catastrophi ...
... The effective control of the vortex shedding behind the cylinders becomes an important issue due to their wide range of practical applications like flow past heat exchangers, buildings, suspension bridges, road vehicles to name a few. The vortex shedding the bluff bodies can sometimes be catastrophi ...
study on impact forces of the underwater cavity projectile
... the longitudinal axis of the projectile. The components of velocity V of point A along the X1 and Z1 directions are U and W, respectively. The rotational velocity about the Y1 – axis is Q. - At the time the projectile tail impinges on the cavity wall, the cavity axis is very little to change. The an ...
... the longitudinal axis of the projectile. The components of velocity V of point A along the X1 and Z1 directions are U and W, respectively. The rotational velocity about the Y1 – axis is Q. - At the time the projectile tail impinges on the cavity wall, the cavity axis is very little to change. The an ...
flow around wall-mounted cylinders with different geometries
... cross-section of the wind tunnel. The aerodynamic wind tunnel is also of closed return type. The nozzle exit cross-section has a width of 1.87 m in the horizontal direction and a height of 1.4 m in the vertical direction (contraction ratio 5:1). The turbulence level of this tunnel is ...
... cross-section of the wind tunnel. The aerodynamic wind tunnel is also of closed return type. The nozzle exit cross-section has a width of 1.87 m in the horizontal direction and a height of 1.4 m in the vertical direction (contraction ratio 5:1). The turbulence level of this tunnel is ...
Fundamentals of Flight - Aviation Training Network
... In forward flight, air flows opposite the flight path of the aircraft. The velocity of the flow of air equals the forward speed of the helicopter. Because the blades of the helicopter turn in a circular pattern, the velocity of the airflow across a blade depends on the position of the blade in the r ...
... In forward flight, air flows opposite the flight path of the aircraft. The velocity of the flow of air equals the forward speed of the helicopter. Because the blades of the helicopter turn in a circular pattern, the velocity of the airflow across a blade depends on the position of the blade in the r ...
LAB 07: What does Friction Depend on and Mμ
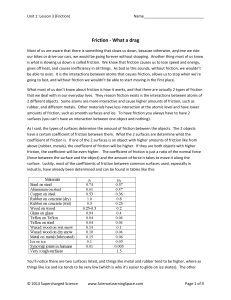
... Coefficient of friction (μ): a quantity used to determine the amount of friction between two surfaces Ffriction = * Fnormal ...
... Coefficient of friction (μ): a quantity used to determine the amount of friction between two surfaces Ffriction = * Fnormal ...
nose cone design
... Comparison of drag characteristics of various nose cone shapes in the transonic to lowmach regions. Rankings are: superior (1), good (2), fair (3), inferior (4). In many nose cone designs, the greatest concern is flight performance in the transonic region from 0.8 to 1.2 Mach. Although data is not ...
... Comparison of drag characteristics of various nose cone shapes in the transonic to lowmach regions. Rankings are: superior (1), good (2), fair (3), inferior (4). In many nose cone designs, the greatest concern is flight performance in the transonic region from 0.8 to 1.2 Mach. Although data is not ...
ent 257/4 fluid mechanics
... Two dimensional Flow: When the dependent variables in a fluid flow vary with only two space coordinates, the flow is said to be two dimensional. The flow does not vary along the third coordinate direction Example: The flow around a circular cylinder of infinite length (as shown in Fig. 2c) is two ...
... Two dimensional Flow: When the dependent variables in a fluid flow vary with only two space coordinates, the flow is said to be two dimensional. The flow does not vary along the third coordinate direction Example: The flow around a circular cylinder of infinite length (as shown in Fig. 2c) is two ...
Design of NACA 2412 and its Analysis at Different
... Abstract—The purpose of this project is to analyze airfoil at different Reynolds numbers using Gambit and Fluent, and wind tunnel experiment. One model is prepared for wind tunnel analysis and 2D and 3D models are created and drawn in solid work and they were meshed in Gambit using geometry data gat ...
... Abstract—The purpose of this project is to analyze airfoil at different Reynolds numbers using Gambit and Fluent, and wind tunnel experiment. One model is prepared for wind tunnel analysis and 2D and 3D models are created and drawn in solid work and they were meshed in Gambit using geometry data gat ...
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) refers to forces acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, drag forces depend on velocity.Drag force is proportional to the velocity for a laminar flow and the squared velocity for a turbulent flow. Even though the ultimate cause of a drag is viscous friction, the turbulent drag is independent of viscosity.Drag forces always decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path.