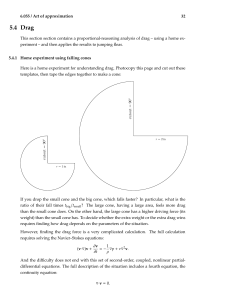
Flow over immerse bodies
... When any body moves through a fluid, an interaction between the body and the fluid occurs; this effect can be described in terms of the forces at the fluidbody interface. This can be described in terms of the stresseswall shear stresses, due to viscous effects and normal stresses due to the pressure ...
... When any body moves through a fluid, an interaction between the body and the fluid occurs; this effect can be described in terms of the forces at the fluidbody interface. This can be described in terms of the stresseswall shear stresses, due to viscous effects and normal stresses due to the pressure ...
Concept of Drag
... If you know the velocity at each time step and the drag force at each time step, you can plot F versus v2 and fit a straight line to the data. Care must be taken to make sure you line up the correct force (a 1x6 array) with the correct velocity (a 1x8 array). Force 1 matches velocity 2, etc. ...
... If you know the velocity at each time step and the drag force at each time step, you can plot F versus v2 and fit a straight line to the data. Care must be taken to make sure you line up the correct force (a 1x6 array) with the correct velocity (a 1x8 array). Force 1 matches velocity 2, etc. ...
Aerodynamics Notes 2
... Drag= Cd x q x A There is a similarity between lift coefficient and drag coefficient in that the lift coefficient, CL , is a measure of how much of the dynamic pressure gets converted into lift, and the drag coefficient is a measure of how well a wing (or other body) converts dynamic pressure force ...
... Drag= Cd x q x A There is a similarity between lift coefficient and drag coefficient in that the lift coefficient, CL , is a measure of how much of the dynamic pressure gets converted into lift, and the drag coefficient is a measure of how well a wing (or other body) converts dynamic pressure force ...
Dragedit - Physics Forums
... dependent on two complex factors; drag pressure and drag friction. We can however say “As the size and/or speed of the body increases, in due course the flow of fluid past the body becomes disorderly and turbulent. For example the, the flow of air past an automobile moving 100 km/h is quite turbulen ...
... dependent on two complex factors; drag pressure and drag friction. We can however say “As the size and/or speed of the body increases, in due course the flow of fluid past the body becomes disorderly and turbulent. For example the, the flow of air past an automobile moving 100 km/h is quite turbulen ...
Fluid Power Resistance - U
... and its applications • Define laminar and turbulent flow • Explain viscosity and how it is measured ...
... and its applications • Define laminar and turbulent flow • Explain viscosity and how it is measured ...
OH 5: Fluid Dynamics
... All athletic events take place in a fluid environment water (swimming), air (cycling), both (water polo) ...
... All athletic events take place in a fluid environment water (swimming), air (cycling), both (water polo) ...
amee401
... Two smooth spheres are attached to a thin rod that is free to rotate in the horizontal plane about point O as shown in the Figure. The rod is held stationary until the air speed reaches 15.24 m/ s . Which direction will the rod rotate (clockwise or counterclockwise) when the holding force is release ...
... Two smooth spheres are attached to a thin rod that is free to rotate in the horizontal plane about point O as shown in the Figure. The rod is held stationary until the air speed reaches 15.24 m/ s . Which direction will the rod rotate (clockwise or counterclockwise) when the holding force is release ...
Teacher Guide
... the kite is airborne and stable, a spring is used to measure the force being exerted by air. Then using the drag equation, the wind velocity was determined. The lesson starts with a comparison of the two flying objects, i.e., an airplane and a kite. In order to understand forces, a free body diagram ...
... the kite is airborne and stable, a spring is used to measure the force being exerted by air. Then using the drag equation, the wind velocity was determined. The lesson starts with a comparison of the two flying objects, i.e., an airplane and a kite. In order to understand forces, a free body diagram ...
Fluids
... If the swirling is regular and repeatable, it is termed a vortex or an eddy The region in the BL where the orderly laminar layers start to mix together, but before they really start swirling, is called the transition region. The transition region is usually in a fairly small region. ...
... If the swirling is regular and repeatable, it is termed a vortex or an eddy The region in the BL where the orderly laminar layers start to mix together, but before they really start swirling, is called the transition region. The transition region is usually in a fairly small region. ...
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) refers to forces acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, drag forces depend on velocity.Drag force is proportional to the velocity for a laminar flow and the squared velocity for a turbulent flow. Even though the ultimate cause of a drag is viscous friction, the turbulent drag is independent of viscosity.Drag forces always decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path.