An Aerodynamicist`s View of Lift, Bernoulli, and Newton
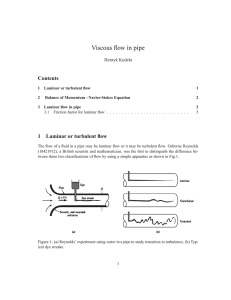
... Most single-engine Cessna aircraft have used this airfoil since the 1940s, which almost certainly makes it the most widely used airfoil in the world. The equaltime-of-passage picture of lift-producing flow patterns leads to the seemingly logical yet incorrect conclusion that this airfoil could not p ...
... Most single-engine Cessna aircraft have used this airfoil since the 1940s, which almost certainly makes it the most widely used airfoil in the world. The equaltime-of-passage picture of lift-producing flow patterns leads to the seemingly logical yet incorrect conclusion that this airfoil could not p ...
The No-Slip Boundary Condition in Fluid Mechanics
... that flow velocity in the channel is sufficiently small. This is a brave conclusion in spite of the cautious qualification. It is quite possible he was influenced by the model of a rolling ball (see Box 1 in Part 1) which may roll without slipping at low velocities but may slip at higher velocities. ...
... that flow velocity in the channel is sufficiently small. This is a brave conclusion in spite of the cautious qualification. It is quite possible he was influenced by the model of a rolling ball (see Box 1 in Part 1) which may roll without slipping at low velocities but may slip at higher velocities. ...
Materials - UCSI A
... Measure the masses in kilograms of a wide range of solid objects. Then measure their voumes. Use a micrometer or vernier callipers to measure their dimensions if they are regular, or use the method of displacement of a volume of water by a solid with irregular shape. The density can be calculated by ...
... Measure the masses in kilograms of a wide range of solid objects. Then measure their voumes. Use a micrometer or vernier callipers to measure their dimensions if they are regular, or use the method of displacement of a volume of water by a solid with irregular shape. The density can be calculated by ...
Velocity Profiles for Circular Sections and Flow in
... • The validity of this substitution can be demonstrated by calculating the hydraulic radius for a circular pipe: ...
... • The validity of this substitution can be demonstrated by calculating the hydraulic radius for a circular pipe: ...
FLUID MECHANICS PART II(1)
... This principle states that a body wholly or partially immersed in fluid is buoyed up with a force which is equal to the weight of the volume of fluid the body displaces and which acts vertically upwards through the centre of gravity of the immersed part of the body. The buoyancy force need not act t ...
... This principle states that a body wholly or partially immersed in fluid is buoyed up with a force which is equal to the weight of the volume of fluid the body displaces and which acts vertically upwards through the centre of gravity of the immersed part of the body. The buoyancy force need not act t ...
Flow velocity and volumetric flow rates are important quantities in
... Moreover, only the flow velocity component parallel to the surface normal of the surface in question, or alternatively the flow velocity component perpendicular to the surface in question contributes to the volumetric flow rate. Figure 1 and Equation 2 illustrate decomposition of the flow velocity v ...
... Moreover, only the flow velocity component parallel to the surface normal of the surface in question, or alternatively the flow velocity component perpendicular to the surface in question contributes to the volumetric flow rate. Figure 1 and Equation 2 illustrate decomposition of the flow velocity v ...
Fluid Flow - Binus Repository
... Asymmetric bed forms (see next chapter) develop similar eddies. ...
... Asymmetric bed forms (see next chapter) develop similar eddies. ...
Computational Simulation of a Heavy Vehicle Trailer Wake
... is due, in part, to the function of a heavy vehicle, which is designed to carry as much cargo as possible. Thus, the shape of the cargo-carrying portion of the heavy vehicle is boxy in nature with many sharp edges. While this shape allows for a large cargo volume and easy access into the cargo bay, ...
... is due, in part, to the function of a heavy vehicle, which is designed to carry as much cargo as possible. Thus, the shape of the cargo-carrying portion of the heavy vehicle is boxy in nature with many sharp edges. While this shape allows for a large cargo volume and easy access into the cargo bay, ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... The solution of fluid flow past solid particles with no-slip boundary condition at the fluid-solid interface is mostly used assumption in fluid mechanics. But the no-slip condition is not valid in case of flow in micro/nano-channels, aerosol particles, flow through porous media and variety of comple ...
... The solution of fluid flow past solid particles with no-slip boundary condition at the fluid-solid interface is mostly used assumption in fluid mechanics. But the no-slip condition is not valid in case of flow in micro/nano-channels, aerosol particles, flow through porous media and variety of comple ...
VISCOSITY - WatchYourSteps
... internal friction called viscosity. It exists in both liquids and gases and is essentially a frictional force between different layers of fluid as they move past one another. In liquids the viscosity is due to the cohesive forces between the molecules while in gases the viscosity is due to collisi ...
... internal friction called viscosity. It exists in both liquids and gases and is essentially a frictional force between different layers of fluid as they move past one another. In liquids the viscosity is due to the cohesive forces between the molecules while in gases the viscosity is due to collisi ...
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) refers to forces acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, drag forces depend on velocity.Drag force is proportional to the velocity for a laminar flow and the squared velocity for a turbulent flow. Even though the ultimate cause of a drag is viscous friction, the turbulent drag is independent of viscosity.Drag forces always decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path.