* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Jordan University of Science and Technology
Soar (cognitive architecture) wikipedia , lookup
Agent (The Matrix) wikipedia , lookup
Visual Turing Test wikipedia , lookup
Turing test wikipedia , lookup
Computer vision wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Human-Computer Interaction Institute wikipedia , lookup
Computer Go wikipedia , lookup
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Wizard of Oz experiment wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Knowledge representation and reasoning wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
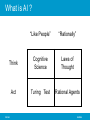
Artificial Intelligence Hassan Najadat Jordan University of Science & Technology CS 362 SLIDE 1 Outline • • • • Course Overview What is AI ? A brief history The state of the art CS 362 SLIDE 2 Course Overview • Intelligent agent • Problem Solving – – – – Solving problems by searching Informed Search and Exploration Constraint Satisfaction Problems Adversarial Search • Logical system – – – – Logical Agent First Order Logic Inference in First-Order Logic Knowledge Representation • Learning from Observations CS 362 SLIDE 3 What is AI ? “Like People” “Rationally” Think Cognitive Science Laws of Thought Act Turing Test Rational Agents CS 362 SLIDE 4 What is AI ? Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationality ``The exciting new effort to make computers think ... machines with minds, in the full and literal sense'' (Haugeland, 1985) ``The automation of activities that we associate with human thinking, activities such as decision-making, problem solving, learning ...'' (Bellman, 1978) ``The study of mental faculties through the use of computational models'' (Charniak and McDermott, 1985) ``The study of the computations that make it possible to perceive, reason, and act'' (Winston, 1992) Systems that act like humans Systems that act like rationality ``The art of creating machines that perform functions that require intelligence when performed by people'' (Kurzweil, 1990) ``The study of how to make computers do things at which, at the moment, people are better'' (Rich and Knight, 1991) ``A field of study that seeks to explain and emulate intelligent behavior in terms of computational processes'' (Schalkoff, 1990) ``The branch of computer science that is concerned with the automation of intelligent behavior'' (Luger and Stubblefield, 1993) CS 362 SLIDE 5 Acting humanly: The Turing Test approach • The Turing Test, proposed by Alan Turing (Turing, 1950), was designed to provide a satisfactory operational definition of intelligence. • The computer would need to possess the following capabilities: 1. 2. 3. 4. • Natural language processing to enable it to communicate successfully in English (or some other human language); Knowledge representation to store information provided before or during the interrogation; Automated reasoning to use the stored information to answer questions and to draw new conclusions; Machine learning to adapt to new circumstances and to detect and extrapolate patterns. To pass the total Turing Test, the computer will need • • CS 362 Computer Vision Robotics SLIDE 6 Example Natural Language (NL) Processing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. • • noun verb determiner adjective adverb pronoun s --> det, noun, verb, det, noun. a better version – s --> np, verb. s --> np, verb, np. np --> det, adj*, noun. np --> proper-name. np --> pronoun. CS 362 SLIDE 7 Thinking humanly: The cognitive modeling approach - Program thinks like a human ..! We need to get inside the actual workings of human minds. There are two ways: – through introspection--trying to catch our own thoughts as they go by— – or through psychological experiments. • GPS -``General Problem Solver'' – (GPS) A procedure and program developed by Allen Newell, J. C. Shaw, and Herbert Simon. – GPS attains an objective by using recursive search and by applying rules to generate the alternatives at each branch in the recursive expansion of possible sequences. – GPS uses a procedure to measure the "distance" from the goal. CS 362 SLIDE 8 Thinking rationality: The Logical approach • Ensure that all actions performed by computer are justifiable (“rational”) Facts and Rules in Formal Logic Theorem Prover • Rational = Conclusions are provable from inputs and prior knowledge • Problems: – Representation of informal knowledge is difficulty – Hard to define “provable” plausible reasoning – Combinatorial explosion: Not enough time or space to prove desired conclusions. CS 362 SLIDE 9 Acting rationally: The rational agent approach • Rational behavior : doing the right thing ( that which is expected to maximize goal achievement, given the available information). • Agent • Program • Agent and Program • Rational Agent is one that acts to achieve the best outcomes or, when there is uncertainty, the best expected outcome. Rational agents do the best they can given their resources CS 362 SLIDE 10 Rational Agents very few resources no thought “reflexes” lots of resources limited, approximate reasoning Careful, deliberate reasoning • Adjust amount of reasoning according to available resources and importance of the result • This is one thing that makes AI hard CS 362 SLIDE 11 CS 362 SLIDE 12 CS 362 SLIDE 13 Areas of Study in AI • Reasoning, optimization, resource allocation – planning, scheduling, real-time problem solving, intelligent assistants, internet agents • Natural Language Processing – information retrieval, summarization, understanding, generation, translation • Vision – image analysis, recognition, scene understanding • Robotics – grasping/manipulation, locomotion, motion planning, mapping CS 362 SLIDE 14 Where are we now? • SKICAT: a system for automatically classifying the terabytes of data from space telescopes and identifying interesting objects in the sky. 94% classification accuracy, exceeds human abilities. • Deep Blue: the first computer program to defeat champion Garry Kasparov. • Pegasus: a speech understanding program that is a travel agent (1-877-LCS-TALK). • Jupiter: a weather information system (1-888-573-TALK) • HipNav: a robot hip-replacement surgeon. CS 362 SLIDE 15 Where are we now? • Navlab: a Ford escort that steered itself from Washington DC to San Diego 98% of the way on its own! • google news: autonomous AI system that assembles “live” newspaper • DS1: a NASA spacecraft that did an autonomous flyby an asteroid. • Credit card fraud detection and loan approval • Search engines: www.citeseer.com, automatic classification and indexing of research papers. • Proverb: solves NYT puzzles as well as the best humans. CS 362 SLIDE 16 Surprises in AI research • Tasks difficult for humans have turned out to be “easy” – – – – – – – – CS 362 Chess Checkers, Othello, Backgammon Logistics planning Airline scheduling Fraud detection Sorting mail Proving theorems Crossword puzzles SLIDE 17 Surprises in AI research • Tasks easy for humans have turned out to be hard. – – – – – – – CS 362 Speech recognition Face recognition Composing music/art Autonomous navigation Motor activities (walking) Language understanding Common sense reasoning (example: how many legs does a fish have?) SLIDE 18