* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Germ disc differentiation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
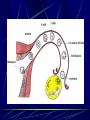
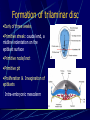
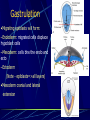
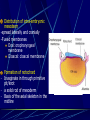
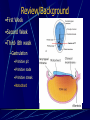
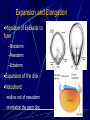
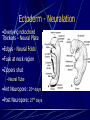
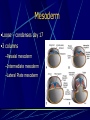
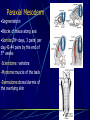
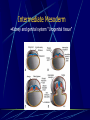
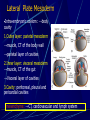
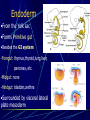
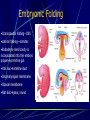
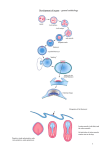
Third to Eighth Week: The Embryonic Period Jun Zhou(周俊) School of Medicine, Zhejiang University 20130108 Review End of the Week of Twos •2 major cell masses –Trophoblasts –Inner cell mass •Trophoblasts –Cytotrophoblasts –Syncytiotrophoblasts Uteroplacental Cir. •Embryonic Cavities –Amniotic cavity –Yolk sac •Germ Disc –Epiblasts –Hypoblasts Formation of trilaminar disc •Early of three weeks •Primitive streak: caudal end, a midline indentation on the epiblast surface •Primitive node/knot •Primitive pit •Proliferation & Invagination of epiblasts Intra-embryonic mesoderm Gastrulation •Migrating epiblasts will form: –Endoderm: migrated cells displace hypoblast cells –Mesoderm: cells btw the endo and ecto –Ectoderm (Note - epiblasts=>all layers) •Mesoderm cranial and lateral extension Distribution of intra-embryonic mesoderm -spread laterally and cranially -Fused membranes Oral: oropharyngeal membrane Cloacal: cloacal membrane Formation of notochord - Invaginate in through primitive pit/knot - a solid rod of mesoderm - Basis of the axial skeleton in the midline Review/Background •First Week •Second Week •Third- 8th week –Gastrulation •Primitive pit •Primitive node •Primitive streak •Notochord Expansion and Elongation •Migration of Epiblasts to form –Endoderm –Mesoderm –Ectoderm •Expansion of the disk •Notochord: -midline rod of mesoderm -orientation the germ disc Differentiation of trilaminar germ disc 3rd –8th weeks embryonic period: the major body form and organ structure take Bilaminar disc: flat and roundelongated with a broad cephalic and a narrow caudal end Trilaminar disc:a pear-shaped appearance Ectoderm - Neuralation •Overlying notochord Thickens – Neural Plate •Edges - Neural Folds •Fuse at future neck region •Zippers shut –Neural Tube •Ant/Post Neuropores Ectoderm - Neuralation •Overlying notochord Thickens – Neural Plate •Edges - Neural Folds •Fuse at neck region •Zippers shut –Neural Tube •Ant Neuropore: 25th days •Post Neuropore: 27th days Ectoderm – Neuralation •Failure of Neurotube closure –Anencephaly – Ant –Meningocele – post Ectoderm – Neural Crest •As neural tube closes -Neural crest •Detach and migrate –Melanocytes – skin –Dorsal root ganglia Differentiation of the Ectoderm : -the central nervous system (CNS) -Neural crest cells (melanocyte, PNS) In general terms it may be stated that the ectoderm gives rise to those organs and structures that maintain contact with the outside world. Mesoderm •Loose – condenses day 17 •3 columns –Paraxial mesoderm –Intermediate mesoderm –Lateral Plate mesoderm Paraxial Mesoderm •Segmentation •Blocks of tissue along axis •Somite:20th days, 3 pairs/ per day,42-44 pairs by the end of 5th weeks -Sclerotome: vertebra -Myotome:muscle of the back -Dermatome:dorsal dermis of the overlying skin Intermediate Mesoderm •Kidney and genital system “Urogenital tissue” Lateral Plate Mesoderm •Intra-embryonic coelom: →body cavity 1.Outer layer: parietal mesoderm →muscle, CT of the body wall →parietal layer of cavities 2.Inner layer: visceral mesoderm →muscle, CT of the gut →Visceral layer of cavities 3.Cavity: peritoneal, pleural and pericardial cavities mesenchyme: →CT, cardiovascular and lymph system Endoderm •From the Yolk sac •Forms Primitive gut •Besides the GI system -Foregut: thymus,thyroid,lung,liver, pancreas, etc. -Midgut: none -Hindgut: bladder,urethra •Surrounded by visceral lateral plate mesoderm Embryonic Folding •Craniocaudal folding--CNS •Lateral folding—somites •Endoderm-lined cavity is incorporated into the embryo properprimitive gut •Yolk sacvitelline duct •Oropharyngeal membrane •Cloacal membrane •Flat discpear, round 3-8th week OBJECTIVES 1.Bilaminar and trilaminar germ discs 2.Undertand the origin of the three embryonic “germ” layers that make up the trilaminar disk. 3.Describe the formation and derivatives of ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.