* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HOLY SPIRIT - Erskine College
Ethics of eating meat wikipedia , lookup
Moral relativism wikipedia , lookup
Bernard Williams wikipedia , lookup
Cosmopolitanism wikipedia , lookup
Consequentialism wikipedia , lookup
Kantian ethics wikipedia , lookup
J. Baird Callicott wikipedia , lookup
Alasdair MacIntyre wikipedia , lookup
Virtue ethics wikipedia , lookup
Ethical intuitionism wikipedia , lookup
Primary care ethics wikipedia , lookup
Sexual ethics wikipedia , lookup
Aristotelian ethics wikipedia , lookup
Organizational technoethics wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of technology wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Hill Green wikipedia , lookup
Marketing ethics wikipedia , lookup
Compliance and ethics program wikipedia , lookup
Accounting ethics wikipedia , lookup
Morality and religion wikipedia , lookup
Medical ethics wikipedia , lookup
Arthur Schafer wikipedia , lookup
Clare Palmer wikipedia , lookup
Business ethics wikipedia , lookup
Secular morality wikipedia , lookup
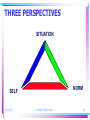
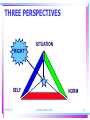
Christian Ethics ETHICS RIGHT WRONG 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 2 ETHICS • ta etheka, the customary, the approved • But- Accepted by Whom? On Whose Authority? 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 3 DEFINITION OF ETHICS • Ethics is “the process of determining right and wrong,” Scott Rae, Moral Choices, 15 • This is a satisfactory definition. However, it is also a definition which can be used by an unbeliever as well as by a Christian 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 4 DEFINITION OF ETHICS • There is a BETTER definition: Ethics is “theology, viewed as a means of determining which human persons, acts, and attitudes receive God’s blessing and which do not.” John Frame, Doctrine of the Christian Life, 1 – This definition assumes the covenantal character of Christian ethics – Because of God’s grace, the believer has been brought into relationship with God, relationship that brings about obligations to love God and to keep his commandments 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 5 DEFINITION OF MORALITY • Morality is “the end result of ethical deliberation, the substance of right and wrong,” Rae, MC, 15 – This is a satisfactory definition – But there is nothing distinctively Christian about it • A BETTER definition: Morality is the end result of the process of “determining which human persons, acts and attitudes receive God’s blessing and which do not.” -John Frame, Ethics Syllabus 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 6 DEFINITION OF VIRTUE • Aristotle, “Virtue is a state of character concerned with choice, lying in a mean, i.e., the mean relatively to us.” Nichomachean Ethics, ix. (Excellence) • In Scripture, arete, areth, Gk., is not a result of formation of habits, the mean between excess and deficiency, but the result of the presence of the grace of God 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 7 DEFINITION OF VIRTUE • Phil. 4:8, “Finally, brothers, whatever is true, whatever is noble, whatever is right, whatever is pure, whatever is lovely, whatever is admirable--if anything is excellent or praiseworthy--think about such things” • II Peter 1:5, “For this very reason, make every effort to add to your faith goodness; and to goodness, knowledge” 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 8 SUMMUM BONUM • For the non-Christian, the highest good assumes the current state of affairs to be normative: What is wrong with this picture? Is the world as it is representative of how God intended it? • For the Christian, the highest good is otherwise: “Man’s chief end is to glorify God and to enjoy him forever.” Shorter Catechism, Q.1 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 9 SUMMUM BONUM • To express this in other terms, Van Til says, “the kingdom of God is man’s summum bonum. By the term kingdom of God we mean the realized program of God for man. . . . The most important aspect of this program is surely that man should realize himself as God’s vicegerent in history.” -Christian Theistic Ethics, 44. 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 10 ETHICS and MORALITY • Most people want to think of themselves as “Good” • Most people would not want to live in a society in which morality is unimportant • Most people face decisions every day that involve questions of right and wrong 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 11 CATEGORIES OF ETHICS • Descriptive Ethics refer to ethics as done from a sociological or anthropological perspective. • This describes Moral Behavior • For a Christian, such ethics may be a worthwhile field for empirical study, but fail to address the imperative of covenantal obedience 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 12 CATEGORIES OF ETHICS • Normative Ethics is “the discipline that produces moral norms or rules as its end product • This prescribes Moral Behavior • This is the “Thus saith the Lord” of Scripture as it directs the hearer of the Word to be a doer of the Word as well 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 13 CATEGORIES OF ETHICS • Metaethics “investigates the meaning of moral language, or the epistemology of ethics,” Rae, MC, 15 • This authorizes and legitimizes Moral Behavior • For the non-Christian, this is a most troublesome issue, for apart from God it is difficult to rationalize a basis for ethical behavior 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 14 CATEGORIES OF ETHICS • Aretaic Ethics “is a category of ethics that focuses on the virtues produced in people, not the morality of specific acts,” Rae, MC, 16. • This links Moral Behavior with Virtue • For Christians, this is spiritual formation • Theologically, this can be viewed as the imperative for relating progressive sanctification to definitive sanctification 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 15 PROBLEM: SOURCE OF ETHICS ABOVE? BELOW? 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 16 ETHICS and METAETHICS • DEONTOLOGICAL SYSTEMS • TELEOLOGICAL SYSTEMS • RELATIVISTIC SYSTEMS 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 17 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Authoritative or Deontological • An authoritative moral source to govern behavior – deon- duty – logos- science, discourse • Transcendent Ethical Norm: – God – Natural Law – Reason 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 18 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Authoritative or Deontological • Definitive standard – Capable of motivating for self-sacrifice – Obligation, but not discerned from sense experience – Ethical Norm imposes duty – Universally binding 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 19 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Authoritative or Deontological • Varieties –Divine Command Theory (“God says it”) –Natural Law (General Revelation) –Ethical Rationalism (a universally binding norm) 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 20 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Authoritative or Deontological • PROBLEM: –May deal just with surface appearances –Fails to consider mitigating circumstances 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 21 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Consequential or Teleological • Assumes the End justifies the Means – telos- end, goal – logos- science, discourse • Immanent Ethical Norm – Mundane – Practical – Doing good brings happiness. The moral life is the good life. 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 22 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Consequential or Teleological • The outcome of actions/behavior makes that action right • Moral Task is to determine the means to the end- happiness • Moral Goodness is concrete, in the situation, not abstracted 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 23 ETHICS and METAETHICS • TELEOLOGICAL SYSTEMS –Utilitarianism (greatest good for greatest number of people) –Ethical Egoism (self-interest determines morality) 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 24 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Consequential or Teleological • PROBLEM: –Often elevates one absolute above all others –Lacks subtlety and flexibility 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 25 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Existential • Assumes there is no objective source for moral propriety • Immanent Ethical Norm is INWARD – True righteousness is never hypocritical – Ethical norm affirmed from within – Judging merely on “externals” is wrong – Moral Law must be MY Law 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 26 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Existential • Each is responsible for the authenticity of his/her actions • Ethical behavior is self-realization – An expression of human nature (Aquinas) – Or, an expression of human freedom (Sartre, and others who deny there is any essential human nature) 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 27 ETHICS and METAETHICS • RELATIVISTIC SYSTEMS – Cultural Relativism (different cultures, different values) – Personal Relativism (I determine right and wrong) – Existentialism (authentic existence determines right choice) – Emotivism (morality expresses feelings about a subject) 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 28 ETHICAL SYSTEMS: Existential • PROBLEM: –Fails to provide a basis for distinguishing moral from immoral behavior 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 29 ETHICS: THREE PERSPECTIVES 1. The Situation What is the dilemma? What is the situation that requires my response? 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 30 ETHICS: THREE PERSPECTIVES 2. Norm What is Right? What does God say? 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 31 ETHICS: THREE PERSPECTIVES 3. Self What is my attitude toward the problem? How do I relate to the situation and the norm? 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 32 THREE PERSPECTIVES SITUATION NORM SELF 5/22/2017 Christian Ethics Part 1 33 THREE PERSPECTIVES SITUATION “RIGHT” SELF 5/22/2017 NORM Christian Ethics Part 1 34 Christian Ethics