* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15
Anglo-Hindu law wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
Classical Hindu law in practice wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Daṇḍa (Hindu punishment) wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
Dayananda Saraswati wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Dharmaśāstra wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
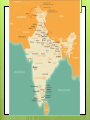
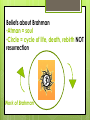
Chapter 15 Learning About Hindu Beliefs Objectives: To discover the origins of Hinduism in ancient traditions and how these beliefs affected life in ancient India and today. I can: • Explain the relationship among Vedic religion, Brahmanism, and Hinduism • Outline the social structure of the caste system • Describe important beliefs in Hinduism and discuss their influence on daily life • Assess the impact of ancient beliefs and practices on life in modern India Vocabulary: • • • • • • • • • Hinduism Vedas Sanskrit Brahmanism caste dharma Karma reincarnation pilgrimage Academic Vocabulary • • • • • affect specific interpret divine cycle Dharma: • Law, obligation, duty To follow one’s dharma: • to perform one’s duties and so to live as one should What would your dharma be? Dharma usually means “right conduct or behavior”. But remember that what is right conduct for a king may well be quite different from what is right conduct for a farmer. •Hinduism is a religion that developed over time from ancient Indian traditions. •Its followers have many beliefs, deities, and practices that differ from place to place. Sacred text: • Ramayana • Tells about life in ancient India • Offers models in dharma Central Figure: • Rama • Lives by the rules of dharma • Young boy = loyal son • Adult= loving husband, responsible ruler Key Hindu Beliefs: Brahman Deities Karma Samsara Dharma 15.2 •Aryans brought the first parts/elements of Hinduism to India •All Hindus follow the basic beliefs of Hinduism that are laid out in the Vedas. 15.2 the Origins of Hinduism (Key Terms) •Vedas – Early Hindu religion which included sacred texts, hymns, and prayers •Sanskrit – An ancient language of India… The Vedas were written in Sanskrit. •Brahman – A class of priests or religious scholars that interpret the Vedas. •Brahmanism – Vedas develop into Brahmanism after the Brahman priest bring a standard way of worshipping the Vedas. 15.3 The Caste System •The way society was organized •Way of life •Four main social classes known as varna Brahmins (priests) Kshatriyas (Rulers, warriors) Vaishyas (Herders, merchants) Shudras (servants, farmers, laborers) Untouchables (out of caste/outcast) •Born into a certain caste •Could never be changed •Could only marry in their own caste Turn & Talk 1. Can you identify each caste correctly? 2. What is each caste’s dharma? 3. What does the middle picture represent? Beliefs about Brahman •Atman = soul •Circle = cycle of life, death, rebirth NOT resurrection Work of Brahman Samsara: •The cycle of birth, death and rebirth Law of Karma: •the good and evil done in a person’s past life determines what happens to one’s soul in the next life •Determines a person’s caste •As long as people are a part of samsara, = people will know pain, suffering and death •Reincarnation: when a person’s soul is reborn into a new body after death •Samsara ends when the soul escapes from the cycle of rebirth. • reunited with Brahma, the supreme force of the universe •Pilgrimages: a journey to a holy place •People travel to sacred places like the Ganges River •Believe the difficulty of the journey would cleanse them of their sins •As Brahma (the Creator), •Vishnu (the Preserver), •Shiva (the Destroyer) Together known as the Trimurti (3 forms) http://www.iskcondesiretree.net/group/krishnaconsciousness/forum/topics/lord-brahma-part-3-1 Shiva (destroyer) Vishnu preserver Swastika The swastika is an ancient symbol that has been found worldwide, but it is especially common in India. Its name comes the Sanskrit word svasti (sv = well; asti = is), meaning good fortune, luck and wellbeing. The swastika is most commonly used as a charm to bring good fortune (in which case the arms are bent clockwise), but it has a variety of religious meanings as well. http://www.religionfacts.com/hinduism/symbols/swastika.htm What connections can you make from what we have studied previously? Hinduism