* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plants - Cloudfront.net
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
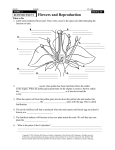
Warm-up 2-22-06 • Do you think you could survive on this planet without plants? Explain.. The Energy Pyramid Autotrophs • An autotroph is an organism that can produce their own food • Plants are autotrophs because they make their own food using sunlight - their cells are designed for this, as they have chloroplasts, an organelle that only plant cells have Heterotrophs An organism that cannot make their own food is called a heterotroph. Examples: people, rabbits, lady bugs, birds, dogs, cats, etc… • The caterpillar is a heterotroph. To live, grow, and perform other caterpillar functions it needs energy from the plant’s sugars. Caterpillars are heterotrophs Caterpillar eating a leaf.. So how do plants make their own food? In a process called photosynthesis PHOTOSYNTHESIS • Plants take up carbon dioxide (CO2) and release oxygen (O2) back into the air • Humans breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide Plant Cell Chloroplasts- site of photosynthesis; this is where energy from sunlight is captured to make food for the plant • Carnivore- an animal that eats meat only • Herbivore- an animal that eats only plants • Omnivore- an animal that eats both plants and animals Energy Pyramid • So, do you think you could survive on this earth without plants? Explain.. Did you get it? Plants are ______because they make their own food. Plants are autotrophs because they make their own food. A cow is an example of a/an__________because it cannot make its own food. A cow is a heterotroph because it cannot make its own food. It needs to eat plants to get energy to survive. • Photosynthesis takes place in the_____________. chloroplasts A bird eating a ladybug that nibbles on a leaf of a plant, is an example of a _______ consumer. secondary consumer What three things are needed for photosynthesis to take place? sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide Add to your flip packet • • • • • Autotrophs Heterotrophs Photosynthesis Carnivore, omnivore, and herbivore Energy Pyramid 1. Flips must include definitions. 2. Flips must include a sentence using the word. 3. Flips must include a picture representing the word. 4. Flips need to have color and be neat. -5 points for each of the criteria Objectives • To distinguish between the male and female parts of a flowering plant • To understand what is pollination and how to know the ways in which plants are pollinated Types of Plants Seed Plants • Gymnosperms are tree shrubs that do not have flowers • Angiosperms are plants that have flowers and seeds that are protected by fruit Seedless Plants • Seedless vascular plants, example- fern, horsetails, and club mosses • Non vascular plants such as liverworts and hornworts Pollination • Pollination is when the pollen is released from the anther and fertilizes the ovule in the ovaries Anthers contain pollen (sperm) and the ovary contains the egg Reproductive Parts Male • Filament- holds the anthers • Pollen-found in the anthers; contains sperm • Anthers- tip of the filament- contains pollen Female • Stigma- sticky part that traps in pollen and pulls it downward • Style- part of the plant that pollen travels down to reach the egg • Ovule- becomes the seed when fertilized by sperm in pollen • Ovary- stores the ovule;part of the flowert hat develops into the fruit A fruit is a ripened ovary that encloses one or more seeds.. How is a plant pollinated? 1. People can transfer pollen from one flower to another, but most plants pollinate without the help from people. 2. Usually they rely on animals, such as birds, bees, flies, and other insects to pollinate them. • The animals don’t mean to pollinate the plants- it happens accidentally. When they go to the base of the petal to get food (nectar) some of the sticky pollen rubs off on them, and they carry it with them to the next plant they feed off of. Then some of the pollen on them can rub off onto the stigma of another plant and fertilize its ovules. Bees pollinating a flower.. A butterfly looking for nectar.. will pollinate a flower without knowing it. Energy Pyramid • The zygote then begins to develop into the seeds embryo • As the seed develops, the ovary changes into the fruit • What are the male parts of a plant? • What are the female parts of a plant? • Which part of the plant becomes the fruit? • What is pollination? Explain..