* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Plantae The Diversity of Plants - Biology102-104
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
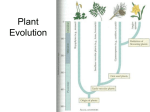
Moss exhibiting gametophyte and sporophyte stages. Fig. 23-5b, p. 372 Evolved supporting structures Conserve water (vessels that transport water and nutrients to all parts of the plant) Dispersal of gametes and zygotes independent of water Roots or root like structures Waxy cuticle Stomata The most widespread group of plants have: Especially well-protected and well-provisioned embryos Waterless dispersal of sex cells Pollen, seeds In flowering plants: flowers and fruits Sori on fern Seeds in Papaya Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Require moist environment to reproduce Straddle aquatic and terrestrial life Vascular plants Able to move to drier habitats Lack true roots, leaves, and stems Have rhizoids which are root-like anchoring structures that bring water and nutrients to plant body Lack well-developed structures for conducting water and nutrients Gametophyte stage most prominent Require water for reproduction Size is limited Acquire water by either slow diffusion or poorly developed conducting tissues to distribute water and nutrients Lack stiffening agent Most are less than 1 inch Liverworts Hornworts Moss Have vessels (specialized conducting cells) Vessels contain lignin (stiffening substance) Above structures allow this group to grow taller Diploid sporophyte is larger than in bryophytes In bryophytes the haploid gametophyte is more evident Seedless plants Seed plants Like bryophytes, have swimming sperm and require water for reproduction Propagate by spores 3 groups Club mosses Horsetails Whisk ferns Ferns Small – few inches tall Leaves are small and scale like Genus Lycopodium – ground pine Most less than 3 feet tall Genus Equisetum Leaves are tiny scales on branches Called “scouring rushes” Deposit large amounts of silica in their outer layer of cells – produce abrasive texture Most diverse of group In tropics, grow very tall Haploid spores produced in sporangia which form on special leaves of the sporophyte Spores dispersed by wind Give rise to tiny haploid gametophyte plants, which produce sperm and eggs As in bryophytes, gametophytes lack conducting vessels and the sperm must swim through water