* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Plantae - Cloudfront.net
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
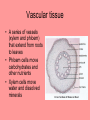
Kingdom Plantae Characteristics of Plants • Eukaryotes • Autotrophs (producers) • Multicellular • Cell walls made of cellulose • 2nd most complex kingdom – May have evolved from algae Vascular tissue • A series of vessels (xylem and phloem) that extend from roots to leaves • Phloem cells move carbohydrates and other nutrients • Xylem cells move water and dissolved minerals Classification of Plants • Bryophytes – – – – Mosses, liverworts Reproduce by spores Nonvascular Require standing water for reproduction Bryophyte life cycle • Gametophyte dominates the life cycle • Male plant produces sperm that swim to the female plant • Requires free water for fertilization • Sporophyte grows from the female plant Classification of Plants • Seedless vascular plants – Ferns, club mosses, and horsetails • Require free water for fertilization • Reproduce with spores Fern life cycle • The diploid sporophyte dominates the fern life cycle • Sori produced on the sporophyte contain spores • Gametophyte germinates and produces antheridia and archegonia • Sperm from the antheridia swim to eggs in the archegonia Modifications to live on land • In order to move away from water, plants must produce seeds in protected structures • Gymnosperms are cone bearing plants • Separate male and female cones Flowering plants • Most plants are angiosperms • Flowers are the reproductive part of the plant – Some have separate male and female plants – Some have male and female flowers on the same plant – Most have flowers with male and female parts Flowering plants • The male part is the stamen – anther – filament • The female part is the carpel (or pistal) – Stigma – Style – Ovary Life Cycle of Angiosperms Flowering plants • The ovary of the flower ripens and becomes a fruit Fruits have different forms Their purpose is seed dispersal: Edible fruit, parachutes, stickers, and floating fruit are just a few of the strategies Angiosperm classification • Divided into two groups: – Monocots – Dicots • Named for number of seed leaves • Other differences include – Organization of vascular tissue – Flower parts – Germination of seed Cross section of a monocot leaf showing parallel veins (vascular tissue) Cross section of a dicot leaf showing mid vein. • • • • A. xylem B. phloem C. upper epidermis D. lower epidermis Leaf structure • Different cells have different functions. • The cuticle and epidermis protect. Leaf structure • Different cells have different functions. • The cuticle and epidermis protect. • Palisade cells photosynthesize. Leaf structure • Different cells have different functions. • The cuticle and epidermis protect. • Palisade cells photosynthesize. • Spongy cells contain air spaces. Leaf structure • Guard cells open and close to regulate gas exchange and water loss.