* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
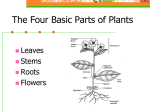
KINGDOM PLANTAE Challenges to moving to land How to obtain water How to prevent water loss Reproduction Getting needed nutrients Non vascular Algae Mosses Hornworts Vascular Plants Fern Gymnosperms Angiosperms GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS Ancestors of today’s land plants were green algea Hundreds of thousands of species in all environments Eukaryotic, multi-cellular organisms Cuticle cover plant that prevents water loss Stomata – openings in plant that facilitate gas exchange Photosynthesis – gas exchange, 02 and C02 that produce energy in the form of sugar C6H1206 + 02 General Characteristics Male gametophyte – Antheridia produce sperm Female gametophyte – Archegonia produce egg Zygote produce by egg and sperm fusion All Plants Have Alternation Of Generations Gametophyte (N) Haploid - Sporophyte (2N) Diploid Non vascular plants Three phyla, collectively called bryophytes Small Need water for reproduction No true roots, stems or leaves Seedless No vascular tissue Mosses Phylum Bryophyta – Mosses 16,000 species Rootlike Rhizoids – absorb nutrients, water Antherdia and archegonia both present on many mosses Typical alternation of generation life cycle Haploid generation dominant Peat moss (sphagnum) Dead cells hold water – used in poor soil conditions Liverworts Phylum Hepatophyta – liverworts, 6,000 species Thallus (thalli resemble liver) – flattened lobe structure of plant Gametophyte dominant generation Hornworts Phylum Anthocerophyta – Hornwarts, 100 species Sporophyte is “needlelike”, grows out of gametophyte – gives rise to the name hornwort Sporangium release spores – grow to gametophytes Seedless Vascular Plants Have vascular tissue, xylem and phloem that provide support and conduction Xylem – conducts water from roots to stems and leaves Phloem – transports food in any direction Have true stems, leaves and roots Club Mosses Phylum Lycophyta – Club Mosses, 1200 species Evergreens – sometimes used in christmas decorations Ferns Phylum Pteridophyta – ferns, 11,000 species Found in swamps, marshes, woodlands, fields, some arctic and aquatic species Alternation of generation life cycle – sporophyte is dominate generation Parts of Ferns Rhizomes - horizontal underground stem Fronds – compound leaves form from rhizomes Fiddlehead – tightly coiled young frond Sorus – cluster of sporangia on the underside of frond that produce spores Antheridia and Archegonium are produced by Fern Parts Fiddlehead Frond Sorus Wisk Ferns Phylum Psilophyta – Wisk ferns, 12 species Mainly in tropics No true roots, rhizomes Sporangia at tip of stems produce spores Horsetails Phylum Pteridophyta Horsetails – grow in wet, moist areas Seed Plants Two types of seed plants are: Gymnosperm – “naked seed” seed usually not enclosed in ovary - examples are: Ginko tree Pine tree Cycads Seed Plants cont. Angiosperms “covered seed” Seed enclosed in ovary, flowering plants – examples are: oak magnolia corn grass Seed Plants Seed plants are superior to spore plants in three ways, they are: 1. The seeds are protected by a seed coat 2. Seeds contain young plant with roots, leaves, and stem 3. Seed contains food supply so after germination embryo is nourished Gymnosperms Gymnosperms consist of pines, fir, spruce, hemlock Sequoia Redwood Bristlecone 77 foot girth tallest 364 oldest 5000 yrs Gymnosperms – seed plants Phylum Coniferophyta (conifers) – pines, firs, spruce, cedar, redwood Redwoods and giant sequoia and the earths tallest trees Most are evergreen, few shed leaves Seeds are stored in female cones, and sperm in the male cones Conifers Importance – food, shelter, wood, paper, drugs, landscaping, turpentine – 630 species Male life cycle female Cycads Phylum Cycadophyta – cycads – 100 species Most species extinct – separate sexes Tropical and subtropical Stout trunk like stems, leaves resemble palms Popular ornamentals, many endangered Ginkgo Phylum Ginkgophyta – one living species Separate sexes, female tree seed gives off rancid odor Leaves bright yellow, deciduous (leaves fall off) Ginko biloba – taken to improve memory Gnetophytes Phylum Gnetophyta – vines, shrubs, and trees Grow in desert and tropical climates Jointed stems, some resemble horsetails Ephedra used to treat high blood pressure and was used for dieting Angiosperms Angiosperms – “covered seed” flowering plants Phylum Anthophyta – 300,000species Most successful of all plants Small to large – violets and eucalytus tree Reproduce sexually –flowers - form seeds within fruits Xylem tissue has vessel elements for conducting water Phloem tissue has sieve tube elements for conducting sugar Economic value All major food crops are angiosperms Rice, wheat, barley, corn Valuable lumber – oak, walnut, etc Cotton and linen Wheat Rice Corn Phylum Anthophyta Class Monocotyledons – monocots – 90,000 species One cotyledon - embryonic seed leaf Parallel venation Scattered vascular bundles Flower parts in multiples of 3 Endosperm – nutritive tissue in seed Herbaceous Palms, grasses, orchids, irises, onions and palms Monocotyledons - Monocots Dicotyledones - Dicots Differences in Monocots and Dicots Feature Flower parts Leaf venation Vascular bundle Roots Secondary growth Seeds Monocot 3’s parallel scattered fibrous absent one cotyledon Dicot 4’s netted in a circle taproot present two cotyledons Differences in Monocots and Dicots Flower Parts Sepals, petals, stamens, and Pistil 1. complete flowers have all 4 parts 2. incomplete flowers are missing at least one 3. flowers are the reproductive shoots 4. perfect flowers have both stamens and pistil 5. imperfect flowers have stamen or pistil, but not both Flower Diagram Plant Kingdom Structure and Growth Almost all plants have roots, stems, and leaves Plants range in size and shape Non woody plants (herbaceous) do not produce lignin - Herbaceous plants – no lignin - Annuals - live one year, corn, garden plants - Biennials – two year cycles, cabbage, queen anne’s lace - Annuals and biennials die at end of season Structure and Growth Annuals – non woody – one year growth Structure and Growth Biennials – two year cycle die after 2 years Structure and Growth Woody plants – trees and shrubs – parts persist - - Perennials – are woody plants and “few” herbaceous plants that live more than two years All woody plants are perennials Some live for 100’s, 1000’s of years Woody perennials that shed leaves are “deciduous” Woody perennials that keep their leaves in cold weather are “evergreens” Structure and Growth Perennials – woody plants live 2 or more years Structure and Growth Plant body consist of the root and shoot system Roots – underground system that absorb water and nutrients Shoots – stems and leaves absorb carbon dioxide Both used in their environment for plants benefit Both made up of different tissue types Structure and Growth Three tissue systems of vascular plants are: system function 1. ground tissue - photosynthesis, storage support 2. vascular tissue - conduction and support 3. dermal tissue - protection, covers plant Tissue Systems/Function of Vascular Plants System Ground Tissue Parenchyma Cells Function Parenchyma storage, starch, oil, water photosynthesis, soft part of plant, secrete resins, hormones Collenchyma Collenchyma support – cell alive at maturity, “strings” in celery, beans Sclerenchyma Sclerenchyma support, usually dead at maturity nuts, fruits, veins of leaf System dermal Tissue Tissue epidermis outermost layer of herbaceous plants Cells epidermal cells guard cells Function protection, prevent water loss regulate stomata System Tissue Dermal periderm (suberin) outer bark of stem & root Cells Function cork waterproof dead at maturity protection cork cambien meristematic cells form new cells cork parenchyma storage Plant Growth - Meristems Two types of plant growth are: primary – increase in stem and root length all woody and non weedy exhibit apical meristem - increase in length in tips of roots, shoots, and buds root tips – protective layer that protect roots secondary – increase in girth of plant – mostly in gymnosperms & woody dicots – tissues that grow are wood and bark lateral meristem – growth along the entire length of stems and root Plant Growth Lateral meristem secondary growth along the entire length of the stem and root vascular cambien – long thin layer of meristematic cells that form thin cylinder in stems and roots – adds more cells to secondary xylem (wood) and to secondary phloem (inner bark) cork cambien – divides and forms cork cells and outer bark, cork and cork parenchyma for storage bark – outermost covering of stems and roots – inner bark is secondary phloem and outer bark is periderm Apical and Lateral Meristems Leaf Structure and Function Leaves are the main structure for photosynthesis and water conservation Leaf shapes are characteristic of different species Nodes – where leaves connect to the stem Leaf Leaf Transpiration – water loss in plants, light, heat, wind, and humidity affect Stomata – openings on leaf that allow gas exchange - blue light wavelength opens stomata - low levels of carbon dioxide open stomata - circadian rhythm – 24 hour biological clock opens stomata Leaf Modified leaves – spines on cacti tendrils of peas and squash modified leaves bulbs of onions and tulips are modified leaves carnivorous plants – pitcher have modified leaves Leaf Arrangement Leaf parts - cuticle – waxy layer of epidermis, prevents water loss - pallisade mesophyll – where photosynthesis occurs - vein – where xylem and phloem located - spongy mesophyll – where diffusion of gases occurs - stomata - opening surrounded by guard cells where gas exchange takes place Parts of Leaf Stems and Transport Provide support, stronger than roots Provide support for leaves and flowers Provide transport of sugar, water and minerals Produce buds that make new stems, leaves and flowers Vascular system throughout stems, leaves, and roots Stems amd Transport woody dicot non-woody monocot Stem Woody plants and secondary growth - only woody dicots and cone bearing evergreens have secondary growth - secondary growth causes an increase in girth of stems and roots - vascular cambien gives rise to secondary growth - primary xylem and phloem are replaced during growth by secondary xylem and phloem - wood Stem - sapwood is the term for younger wood- lighter – wood of conifers - heartwood is older wood in center of tree that isn’t functional - wood of flowering plants - cork cambium produces periderm – bark, cells of periderm contain suberin that make them impenetrable to water, insects, fungus, etc - annual rings determine age Stem Structure Roots Roots Anchor, absorb, conduct water and minerals and food storage Two types of roots are: - taproot – one main root formed from seedling – found in dicots and gymnosperms - fibrous – many roots of similar size – monocots Root cap – protective thimble-like cap – covers root tip Roots Root hairs – increase absorption Epidermis covers root Cortex – parenchyma cells, no collenchyma or sclerenchyma cells Endodermis – inner layer regulate water and nutrients Pith – center of many roots and stems Root Types Prop roots – advantageous roots that develop from branches – grow downward and provide support Root types Buttress root – concentrated and surface root that absorb minerals from rotting leaves – found mainly in tropics Root types Pneumatophores – “breathing roots” – grow from submerged part of root in swampy of tidal environment allowing gas exchange Root Types Epiphytes – aerial roots that anchor plants to bark or branch hydroponics