* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
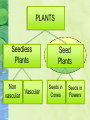
Today’s Agenda… Get your clickers! Bellringer questions Take up homework Create a T-chart to compare seedless vascular and nonvascular plants (SP #3) Notes on Parts of Seed Plants (SP #4) Homework: Worksheet PLANTS Seedless Plants Non vascular Vascular Seed Plants Seeds in Cones Seeds in Flowers Parts of a Seed Plant Study Pack #4 Today’s Goals… I can identify the characteristics of seed plants. I can explain the structure and function of roots, stems, and leaves. Characteristics of Seed Plants Most of the plants you are familiar with are seed plants Most seed plants have leaves, stems, roots, produce seeds, and contain vascular tissue Leaves Organs where photosynthesis takes place Come in many shapes, sizes, colors Figure 14 Leaf Cell Layers Upper and lower surface cells make up the epidermis Covers and protects the leaf A waxy cuticle covers the epidermis Leaf Cell Layers Small openings in the epidermis are called stomata Allow carbon dioxide, water, and oxygen to enter and leave the cell Surrounded by guard cells that open and close Leaf Cell Layers Below the upper epidermis is the palisade Closely packed, long, narrow cells with many chloroplasts Food is made here (photosynethesis takes place here) Leaf Cell Layers Below the palisade is a spongy layer Loosely arranged cells separated by air spaces Vascular tissue is found in this layer Stems Usually above ground Support the braches, leaves, and reproductive structures Materials move between leaves and roots through the vascular tissue Roots Allow water and other substances to enter the plant Act as anchors Support other plant parts that are aboveground Store food What did you learn? Discussion Question How are the structure and function of living things related? THINK PAIR SHARE