* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Cultivation Revision
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
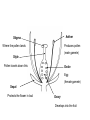
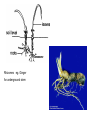
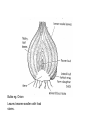
Growing Conditions Factors that a gardener needs to consider to maximise plant growth: • Water • Light – motorised screens, shading • Suitable temperature – greenhouses, polytunnels, cloches, ventilators, fans, fleece • Growing medium (soil, compost etc) • Humidity Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide + water Oxygen + glucose Unhealthy Plant • • • • Wilting – under watering Pest Damage – aphids, slugs Poor Growth Fungal Disease – damping off, potato blight Biological Pest Control • Predator of the pest used to eat the pest • Example: Ladybird is a predator to an aphid • Advantage – No pesticides • Disadvantage – Can change predator-prey relationships, changing the ecosystems K Potassium Mineral Nutrients N Nitrogen P Phosphorus Too much Nitrogen Stem grows too tall and thin and crop falls over Burns the roots N,P,K,Mg • Too much Nitrogen – excess growth, lot of green leaves, not many flowers • Not enough Phosphorous – stunts growth (particularly roots), grow slowly, less resistant to disease or drought • Not enough potassium – edge of leaves yellow/brown, fewer flowers/fruit • Not enough Magnesium – yellow leaves, less healthy, yield lower Fertilisers – absorbed by the roots Organic Inorganic • adds humus and so improves crumb structure • decays slowly so releases nitrogen over a long time • contains large quantities of known amounts of nutrients • cheap and easy to obtain • releases nutrients quickly • contains other nutrients needed by plants such as magnesium • easy to spread Anther Stigma Where the pollen lands Produces pollen (male gamete) Style Pollen travels down this Ovule Egg (female gamete) Sepal Protects the flower in bud Ovary Develops into the fruit Cross Pollination The transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same species This increases genetic variation so plants are able to adapt to their surroundings Self Pollination The transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of the same flower. Advantage Disadvantage Does not require another plant of the same species near by Little genetic variation in offspring Wind Pollinated Plants Feathery Stigma hanging outside the flower to increase surface area to catch pollen Anthers hanging outside the flower so wind will blow pollen away Lots of small, light pollen produced so it can be carried by the wind Flower small and green and not scented since it does not need to attract insects Insect Pollinated Plants Brightly coloured, scented flowers to attract insects Anthers and stigma inside flower in the best position for the insect Small quantities of large, sticky pollen is produced Nectar is produced A word of caution Make sure that there are insects or wind in glass houses and polytunnels Vegetative Reproduction • This is asexual • All offspring are genetically identical to the parents • Growers know what they will produce • If one plant gets a disease they will all get the disease Runners eg. Strawberry plants An above ground stem Rhizomes eg. Ginger An underground stem Bulbs eg. Onion Leaves become swollen with food stores. Seed Germination Testa (Seed Coat) Plumule Tough, so water is needed to swell the seed and break the testa before the seed can germinate Young shoot Radicle Cotyledons (Food Store) Glucose + Oxygen Young root Energy Enzymes are needed for respiration therefore seeds only germinate in the warmth Light is not usually needed for germination except in certain seeds such as lettuce Raising Plants from Seed Growing from seed • Thinning out: weak seedlings removed to give others more room • Pricking out: Lift the seedlings out carefully holding their cotyledons (seed leaves) and re-plant in a new tray to allow seedlings to grow well. • Potting on – give seedlings more room to grow • light sensors • temperature probes • carbon dioxide sensors • pH meters • humidity sensors White Rose Red Rose Phenotype: white Phenotype:Red Genotype: rr Genotype: Rr The allele for red flowers is dominant over the allele for white flowers All the F1 generation are Red Inheritance of Flower Colour Using A Punnet Square A red flowered plant was crossed with a white flowered plant. What is the ratio of phenotypes and genotypes in their offspring? R r R r b r Rr rr b r Rr rr Percentage Genotypes: 1:1 Rr:rr Percentage Phenotypes: 1:1 Red : white Single Digging • aerates the soil • removes weeds • improves drainage • FYM can be added to improve crumb structure • raked to produce a good tilth Clay Water Humus Sand Silt Storing Crops Ripening Bruising Pests Diseases