* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint format
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Ginkgo biloba wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
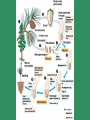
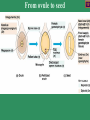
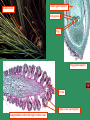
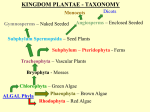
Gymnosperms naked seed Four major living groups. Cycads (Cycadophyta), Welwitschia group (Gnetophyta), Ginkgo, the Maiden Hair Tree (Ginkgophyta), and the conifers (Pinophyta) . Cycas bougainvilleana Cycads Cycads resemble palms or tree-ferns in overall appearance but differ greatly in detailed structure and reproductive behaviour. Cycads are dioecious (i.e. male and female reproductive structures are borne on separate plants), and reproduction is by seeds produced on open carpophylls or seed-bearing leaves. Although technically woody plants, unlike other woody plants, cycads have a thick, soft stem or trunk made up of mostly storage tissue with very little true wood. The living cycads include about 250 species, with 11 genera in 3 families. Microcycas calocoma Photo Dennis Stevenson Female cone Cuban species Gnetophyta Welwitschia mirabilis Lives in coastal desert regions of Namibia and Angola. Morning fogs provide moisture. Female cones Male cones Large, straplike leaves that grow continuously along the ground. During its entire life, each plant produces only two leaves, which often split into many segments as a result of the leaves being whipped by the wind. Carbon-14 datings of the largest plants have shown that some individuals are over 1500 years old. Ginko biloba Illustration in Pen Tsao Kang Mu of Ginkgo with seeds (1578) There are no native ginkgoes living in the wild. Several ginkgoes were the only living survivors of the atomic bomb blast at Hiroshima TeenBodybuilding.com The #1 Site Dedicated to Teenage Bodybuilding! Medicinal!! http://www.teenbodybuilding.com/gingko.htm Today everyone is looking for a way to enhance his or her workouts. Well, as always, make sure your diet and rest is in order. You know the deal, 6 meals per day, at least 7 hours of sleep per night, blah blah, etc blah. So what can you do, well, take some Ginkgo Biloba. What, ginkgo? I thought that was just for old people who couldn't keep a train of thought? Nope, you're wrong. Ginkgo can be a very beneficial herb to bodybuilders as well. Why is Washington called the Evergreen State? The Evergreen State Most conifers are evergreen Evergreens have potential for growth all-year round What is the advantage of the potential for all -year round growth? Why aren’t all plants evergreen? What is the advantage of the deciduous habit over the evergreen habit? Why is so much of Washington covered by evergreen conifers? What is the advantage of the potential for all – year round growth? Opportunistic growth when conditions may be favorable and lack of dependence upon a particular time when growth must be made. Evergreenness Why aren’t all plants evergreen? Evergreen plants are frequently slow growing. The features that enable them to survive harsh conditions do not always enable them to grow quickly. What is the advantage of the deciduous habit over the evergreen habit? Deciduous plants are frequently faster growing than evergreen plants and can rapidly exploit favorable and reliable habitats. Leaves do not require to withstand severe cold and leaf abscission enables nutrients and carbohydrates to be withdrawn into the plant for re-use Why is so much of Washington covered by evergreen conifers? It regularly has periods of summer drought but mild wet winters. This can favor evergreens over deciduous trees. In what other type of environment are evergreen conifers frequently found? Relative numbers of species of major groups of plant across geological time Angiosperms Ferns Mosses Time scale Gnetales Cycads Ginkgos Conifers Origins of conifers in the Permian The coal forming period Millions of years Pangea Gymnosperms show adaptations to drier conditions than mosses and ferns both in their reproduction and vegetative growth Continental type climates typically have dry periods or seasonal rains. These can be seasonal and may be called monsoons In the Permian the land masses came together and formed a large continent call Pangea 360 to 286 mya Carboniferous Adaptations for the drier environment Reproductive 1. Airborne male gametophyte (pollen) carried by wind to the female gametophyte where sperm fertilizes the egg located in the female gametophyte in the ovule which is retained, sustained and protected by the sporophyte. 2. Production of a durable seed that at maturity consists of a protective seed coat, a source of nutrition and an embryo sporophyte all in one package. Vegetative 3. Seed plants have wood producing tissue well developed in some species for water conduction and support. This enables plants to grow tall and out-compete neighbors Reproduction in the conifers The cone is a modified branch. Unlike the flower it does not have sepals or petals. Usually separate male and female cones are borne on the same plant, i.e., monoecious. Each of the numerous scales, or sporophylls, of the male cone bears pollen and each female cone scale bears ovules in which egg cells are produced. . Life cycle Fig. 17.8 From ovule to seed Cedrus deodora The diminutive female cone Male cones – all lined up and ready to go! Developing seed cones Continuing vegetative shoot Pollen grains Male cone Pictures of male cone and pollen Microsporangium Female gametophyte Female cone Archegonia Pictures of female cone Egg Megagametophyte Ovule Single scale (sporophyll Longitudinal section through ovulate cone Bristlecone pine Pinus longaeva Male cone Current year Last year’s empty sporangia Female cone The oldest aged specimen is 5,600 y Sections you need to have read 17.8 and Introduction to Chapter 31 Courses that deal with this topic ESC 200 Trees in Our Environment ESC 221 Dendrology and Autecology