* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Conifers
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pinus strobus wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flora of the Indian epic period wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
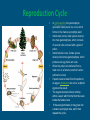
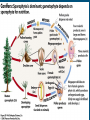
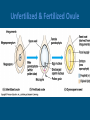
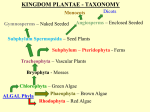
Gymnosperms Gymnosperm • Gymnosperm means “naked seed” – needs the cone to protect it. Female - Megaspores • Cones are reproductive structures of gymnosperm. • Each gymnosperm species has a different cone. • Includes pines, firs, spruces, cedar cycad and gingkoes. • Male and female cones are produced on the same plant. Male – Microspores Structure Roots- anchor the plant into the soil and absorb and send water up the plant for photosynthesis. Pine needles- adaptation in most but not all conifers to function with less water. an example of one that doesn’t have pine needles is the cupressaceae. Structure Stem- houses vascular tissues and supports the rest of the tree. Vascular tissue Specialized tissue in plants that transport water, nutrients and the products of photosynthesis Xylem- primarily for water and nutrients transport, transports water and nutrients up. Phloem- primarily for transport of sugars, transports sugars down and up as needed. Do male and female cones differ? Male and Female Cones Male cones Microspores: smaller and deteriorate quickly,where pollen sheds, less woody texture Female cones Megaspores:The cone scales each carry two ovules that develop to seeds, bigger Reproduction Cycle • • • • • • • In gymnosperms, the gametophyte generation takes place in a cone, which forms on the mature sporophyte plant. Inside male cones, male spores develop into male gametophytes, which consists of several cells enclosed with a grain of pollen Inside female cones, female spores develop into female gametophytes, which produces an egg inside an ovule. When the pollen is transferred from a male cone to a female cone that's when pollination occurs If sperm were to travel from the pollen to an egg so fertilization can occur, a diploid zygote is the result. The zygote develops into an embryo within a seed, which forms from the ovule inside the female cone If the seed germinates, it may grow into a mature sporophyte tree, and it then repeats the cycle. Conifer Conifer, any member of the Pinophyta, class Pinopsida, order Pinales, made up of living and fossil gymnospermous plants that usually have needle-shaped evergreen leaves and seeds attached to the scales of a woody bracted cone. Coniferous means cone bearing. Cones • All conifers bear seeds inside cones, woody protective structures. • The conifers are a group of about 588 species of trees and shrubs that include many of the bestknown plants in the world. • There are seven families of conifers. The largest is the Pine family (232 species), which includes such familiar trees as pine, spruce, fir, and larch. Unfertilized & Fertilized Ovule Conifer – Trees • Almost all conifers are trees, and so they create forests that provide habitat for wildlife and a wide variety of insects, fungi, and smaller plants. • Some conifer forests support extremely complex ecosystems with very high levels of biodiversity. Conifer Forest • Only have two layers • another name for coniferous forest is TAIGA • The canopy layer is made up of tree which grow to a uniform height between 20m to 30m. • Trees grow close together. • The under growth layer has very littler vegetation because of the low amount of sun light and poor fertility of the soil. • Conifer forest mainly found in colder areas, northern potion of the norther hemisphere. Often covering mountainsides. • Over time the demand of life on the land favored the evolution of plants as they are more resistant to the drying rays of the sun, more capable of reproducing without water.