* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
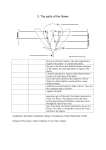
Bell work 1/12/12 Some plants have flowers & some do not. Some flowering plants (plants with flowers) produce fruit. What part of the flower is the fruit? (You may give a specific name or talk about where the part is or what it does.) Objectives • Match the flower parts with their reproductive functions. (SPI 0707.4.2) – Take notes on flower parts – Create a flower foldable Parts of the Flower The Parts of a Flower • Most flowers have four parts: • sepals, • petals, • stamens, • carpels. M A • L E F E M A L E The parts of a flower • Sepals protect the bud until it opens. • Petals attract insects. • Stamens make pollen. • Carpels grow into fruits which contain the seeds. Explain to your elbow partners about the four main parts of a flower and what their function is. Stamen (male) • Anther: pollen grains grow in the anther. • Filament- long thread that holds the anther. • When the grains are fully grown, the anther splits open. Pistil (female) • • • • Stigma Style Carpel (ovary) Ovules (eggs) •Stigma: •Style: •Ovary: contains the ovules •Ovules: the lower part of the pistil that produces eggs in ovules Elbow Partners Pollination • Flowering plants use the wind, insects, bats, birds and mammals to transfer pollen from the male (stamen) part of the flower to the female (stigma) part of the flower. Pollination • A flower is pollinated when a pollen grain lands on its stigma. • Each carpel grows into a fruit which contains the seeds. • Seeds are baby plants!!! Directions for Foldable • Use page 166-172 to color, label, and define the following: – Flower, petal, stigma, style, ovary, pistil, sepal, filament, anther, stamen, seed, fruit, photosynthesis, leaves, & stem Draw, color, label, & define: roots Draw & color: soil/ ground Extra Credit: Draw & color background with the sun, rainwater going into the soil for the roots, & insects, such as bees, going through pollination. 3-2-1 Reflection 3 things I learned… 2 questions I have… 1 way I can relate this lesson to my daily life and how it benefits me…