* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are plants and how are they classified?
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
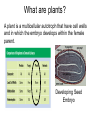
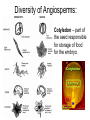
Aim: What are plants and how are they classified? What are plants? A plant is a multicellular autotroph that have cell walls and in which the embryo develops within the female parent. Developing Seed Embryo Origin of Plants: The closest modern relatives of the ancestors of plants are the multicellular green algae (live in water). The evolution of modern plants required many adaptations for the survival of autotrophic organisms on dry land. Adaptations: 1)Roots 2)Stems 3)Leaves Challenges of Life on Land: 1)Obtaining Resources from Air & Soil – algae and other aquatic organisms acquire the resources they need from the surrounding water. Land plants have to obtain resource from land (roots) and air (stems & leaves). Vascular Tissue – vessels responsible for transporting materials from leaves and roots. Challenges of Life on Land: 2)Staying “Afloat” in Air – In an aquatic environment, the buoyancy of water provides physical support for large algae. Lignin is a chemical that hardens the plants’ cell walls and allows them to stand upright on land. Challenges of Life on Land: 3)Maintaining Moisture – Plants have to maintain a moist internal environment even on dry land. • Cuticle – waxy substance that coats the plant to keep in moisture. • Stomata – pores in the leaf surface that allow for gas exchange and regulate water loss. Stomata Guard Cells Challenges of Life on Land: 4)Reproducing on Land – Terrestrial plants require adaptations that ensure that the gametes and the developing embryo will not dry out. Plants must also have some means of dispersal other than water currents **Pollen & Seeds are usually dispersed by wind and animals. Pollen prevents sperm from drying out Seeds prevent embryo from drying out How are plants classified? Bryophytes: 1)First land plants 2)Include mosses 3)Nonvascular plants (grow close to the ground) 4) Lack Seeds Mosses How are plants classified? Pteridophytes: 1)Have Vascular Tissue 2)Lack Seeds 3)Have Lignin in cell walls Ferns How are plants classified? Gymnosperms: 1)Have Vascular tissue 2)Have seeds (plant embryo & food supply) 3)Seeds are “naked” (not enclosed in an ovary) 4) Have Pollen (male sperm) Female Pollen Cone contains Female gamete (egg) Pine Tree How are plants classified? Angiosperms: 1)Have Vascular tissue 2)Flowering plants (flower is a reproductive structure) 3)Have seeds surround by ovaries (fruit) 4) Have pollen Seed Ovary Diversity of Angiosperms: Cotyledon – part of the seed responsible for storage of food for the embryo.